Trump spotted a pattern in China’s standoff with India. Here are 21 reasons
President Donald Trump on Thursday
waded right in the middle of India’s dispute with China, asserting that Beijing’s aggressive stance in Ladakh fits with the larger pattern of Chinese aggression in other parts of the world. President Trump’s office did not elaborate on China’s aggression elsewhere but is seen as a clear reference to Beijing’s efforts to enlarge its position on border disputes. US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo had recently called it China’s “rogue attitude” as he announced the movement of US supercarriers in the Indo Pacific region to counter China’s aggressive posture.
According to Beijing watchers, China has traditionally suffered from xenophobia against foreigners. The Middle Kingdom’s fears were exacerbated in the past two centuries as a result of which China believes that it is the only civilizational power in the world and the rest are either tributary states or barbarians.
China has had territorial disputes with 21 neighbours including India over its claims on land and sea. Here is a complete list of its disputes.
Brunei
China claims the southern part of the Spratly Islands chain. Brunei, on the other hand, claims part of South China Sea nearest to it as part of its continental shelf and Exclusive Economic Zone
Philippines
China and Philippines disagree over parts of the South China Sea including the Spratly Islands. Philippines took the dispute to the International Court of Justice where they won the case but the Chinese side did not abide by the order of the ICJ. Tensions have continued between the two countries despite economic incentives offered by China.
Indonesia
China’s nine-dash line overlaps the Natuna Sea/Exclusive Economic Zone of Indonesia leading to disputes. China claims fishing rights in waters near the islands. Indonesia government argues that China’s claims are not recognised under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. Indonesia irked China in July 2017 when it renamed parts of the South China Sea as North Natuna Sea to underscore its claim.
Malaysia
China’s dispute with Malaysia also revolves around parts of the South China Sea, particularly the Spratly Islands. Its claims cover only islands included in its Exclusive Economic Zone of 200 miles as defined by the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea. Malaysia has a military presence on three such islands that it considers to be part of the continental shelf.
Singapore
Singapore is not a claimant state in the South China Sea disputes but is closely aligned to the United States and allows the presence of US naval forces in Singaporean waters. It does not want to antagonise China by openly taking sides though it does advocate freedom of navigation and resolution of all disputes in line with the UN Convention of Law of the Seas.
Laos
China claims large areas of Laos on historical precedent of China’s Yuan Dynasty during 1271-1368
Cambodia
China has, on occasions, claimed part of the country on historical precedent (China’s Ming dynasty 1368-1644)
Thailand
Thailand opposes China’s dredging on the Mekong River since 2001 for large ships to carry goods from its landlocked Yunnan province to ports in Thailand, Laos and remaining southeast Asia. China has also built hydropower dams on the main stream of the Mekong River, altering the natural flood-drought cycle, affecting ecosystems as well as economies of countries on the lower Mekong River.
The Thai Cabinet scrapped a Chinese-led dredging project in February 2020 to blast rapids on the Mekong river. This had already led to fall in water levels and fers that it would lead to drought and affect 6 million people in Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and Vietnam
Japan
Japan’s dispute with China centers around South China Sea, particularly Senkaku Islands, Ryukyu Islands and the overlapping Air Defence Identification Zone and Exclusive Economic Zone in the East China Sea
Vietnam
Vietnam, which fought a bloody war with China in 1979 when Beijing tried to teach its former ally a lesson, has stood its ground on its territorial claims over parts of the South China Sea, and the Macclesfield Bank, Paracel Islands and the Spratly Islands. Last month, a Chinese ship rammed a Vietnamese fishing boat operating in the Paracel Islands that was seen as an effort by Beijing to flex muscles to enforce a unilateral fishing ban in parts of the South China Sea against vessels from another nation.
India
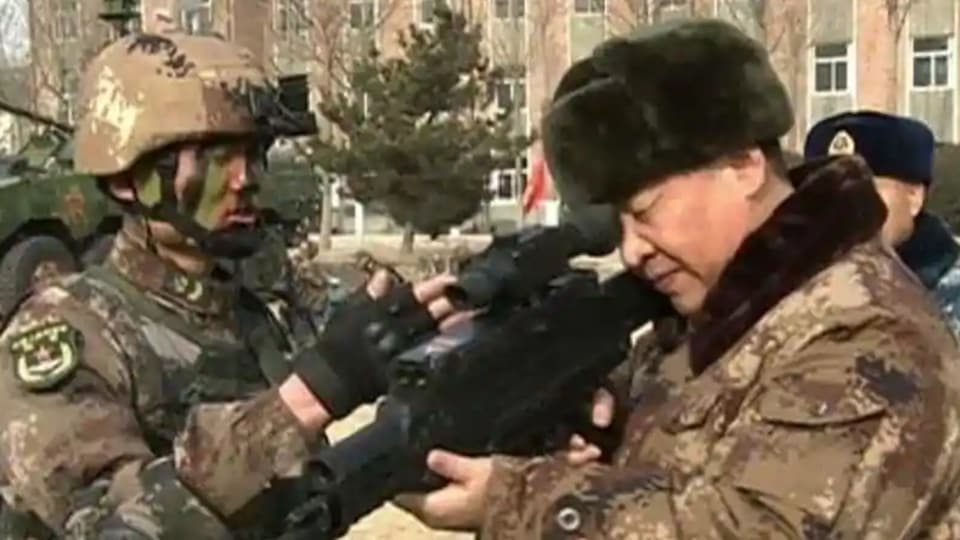
China occupies 38,000 sq km Indian territory in the Aksai Chin region apart from staking claim on Arunachal Pradesh and Ladakh. It was this expansionist policy that led to the ongoing standoff between the Indian Army and the Chinese PLA that escalated into a violent scrap in Ladakh’s Galwan valley. Another 5,163 sq km of Shaksgam valley was illegally ceded by Pakistan to China in 1963. Hence, the total Indian territory occupied by China is over 43 ,000 sq km.
Nepal
Nepal and China have pending border issues over three boundary pillars in Dolakha and two in the vicinity of Mt Everest. There have, however, been reports that China has illegally occupied strategic land at 12 places across Nepal. China has also claimed part of Nepal dating back to the Sino-Nepalese war in 1788-1792, claiming that some parts of Nepal are part of Tibet and therefore, part of China.
Taiwan
China claims all of Taiwan but particular disputes are Macclesfield Bank, Paracel Islands Scarborough Shoal, part of South China Sea and the Spratly Islands. The Paracel Islands, also called Xisha Islands in zvietnamese, is a group of islands in the South China Sea whose sovereignty is disputed.
North Korea
The two countries have a continuing dispute over Mount Paektu and Yalu and Tuman rivers. China has also claimed Baekhu Mountain and Jiandao. Beijing has, on occasions, claimed all of North Korea on historical grounds (Yuan Dynasty 1271-1368)
South Korea
South Korea and China have an overlapping Air Defence Identification Zone and a continuing Exclusive Economic Zone dispute over Leodo (Socotra Rock) in the East China Sea. China has also, on occasions, claimed entire South Korea on historical grounds (Yuan Dynasty 1271-1368)
Mongolia
China and Mongolia have settled their boundary dispute but China has claimed all of Mongolia on historical precedent (Yuan Dynasty 1271-1368).
Bhutan
Bhutanese enclaves in Tibet, namely Cherkip, Gompa, Dho, Dungmar, Gesur, Gezon, Itse Gompa, Khochar, Nyanri, Ringung, Sanmar, Tarchen and Zuthulphuk. Bhutan has lost a substantial chunk of area under dispute including the Kula Kangri peak to slow encroachments by China. Beijing claims Kula Kangri and mountainous areas to the west of this peak in addition to the western Haa district of Bhutan.
Tajikistan
The two sides have a bilateral dispute dating back to 1884 when a border demarcation agreement between the Qing Dynasty and Tsarist Russia left large segments of the frontier in the sparsely-populated eastern Pamirs without a clear definition.
The Chinese claims are based on historical precedent (Qing Dynasty 1644-1912).
In 1991, Tajikistan inherited from the Soviet Union three disputed border segments constituting about 28,000 sq km which China and the Soviet Union had been unable to resolve.
In 1999, Tajikistan and China signed a border demarcation agreement defining the border in two of the three segments. Under this deal, Tajikistan ceded about 200 sw km lands to China. In 2002, Tajikistan agreed to cede 1,122 sq km or about four percent of the territory that Beijing had claimed. China has, in all, settled for 3.5 per cent of the claimed territory.
Kazakhstan
China has laid claim to a territory in Kazakhstan stretching from Semirechie to Lake Balkhash covering 34,000 sq km. In May 2020, a Chinese website ‘Sohu.com’ published an article claiming that Kazakhstan is located on territories that historically belong to China.
China has settled for 22 per cent of its claim over Kazakh territory. Despite a border demarcation treaty with China in 1994 and claim by Kazakh state media that the Kazakhstan government had succeeded in retaining 56.9 percent of the disputed territory, critics had opined that the remaining 43.1 per cent of the land also belonged to Kazakhstan for which a new deal should be signed.
Kyrgyzstan
China lays claim to the whole of Kyrgyz territory. In May 2020, Chinese website tutiao.com published an article on such a claim and argued that under the Han Dynasty, the entire Kyrgyz territory was part of the Chinese mainland before the Russian empire captured it.
Chia has settled for 32 percent of its claim over Kyrgyz territory. Under the 1999 agreement, Kyrgyzstan handed over 1,250 sq km to China.
Russia
Despite signing bilateral agreements in 1991 and 1994 to delimit the estern and wester section of the Russia-China border, a few sectors remain unresolved. There are 160,000 sq km still unilaterally claimed by China despite signing several agreements.
In October 2004, the 4,300 sq border was finally demarcated in its entirety, thus resolving a 300-year-old territorial dispute.
In 2005, the Russian Parliament ratified the agreement in 2008, a part of the Abagaitu Islet, the entire Tarabarov Bolshoi Ussuriysk Island and some adjacent river islets were handed over to China.dusta
India-China standoff: Xi Jinping’s stance in Ladakh fits in the larger pattern of its approach in dealing with its neighbours

www.hindustantimes.com




 .
.
 .. i got my problems jaanu. i m in no mood for war.
.. i got my problems jaanu. i m in no mood for war. . this will stretch their army thin. we will rope in nepal too for added flavor
. this will stretch their army thin. we will rope in nepal too for added flavor

 but whatever.
but whatever.