French offering us nothing better in terms weapon package what we don't have it in MKI
or we are not developing go
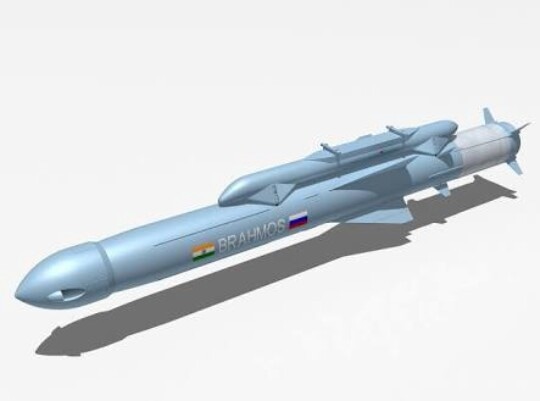
BrahMos-A
The BrahMos-A is a modified air-launched variant of the missile which will arm the Sukhoi PAK-FA of the Indian air force as a standoff weapon. To reduce the missile’s weight to 2.55 tons, many modifications were made like using a smaller booster, adding fins for airborne stability after launch, and relocating the connector. It can be released from the height of 500 to 14,000 meters (1,640 to 46,000 ft). After release, the missile free falls for 100–150 meters, then goes into a cruise phase at 14,000 meters and finally the terminal phase at 15 meters.
BrahMos-NG
BrahMos-NG (Next Generation) is a mini version based on the existing BrahMos, will have same 290 km range and mach 3.5 speed but it will weigh around 1.5 tons, 5 meters in length and 50 cm in diameter, making BrahMos-NG 50 percent lighter and three meters shorter than its predecessor. The system is expected to be inducted in the year 2017. BrahMos-NG will have lesser RCS (radar cross section) compared to its predecessor, making it harder for air defense systems to locate and engage the target. BrahMos-NG will have Land, Air, ship-borne and Submarine tube-launched variants. First test flight is expected to take place in 2017–18. Initially Brahmos-NG was called as Brahmos-M.
BrahMos-II
BrahMos-II is a hypersonic cruise missile currently under development and is estimated to have a range of 290 km. Like the BrahMos, the range of BrahMos II has also been limited to 290 km to comply with the MTCR. With a speed of Mach 7, it will have double the speed of the current BrahMos missile, and it will be the fastest hypersonic missile in the world. Development could take 7–8 years to complete.
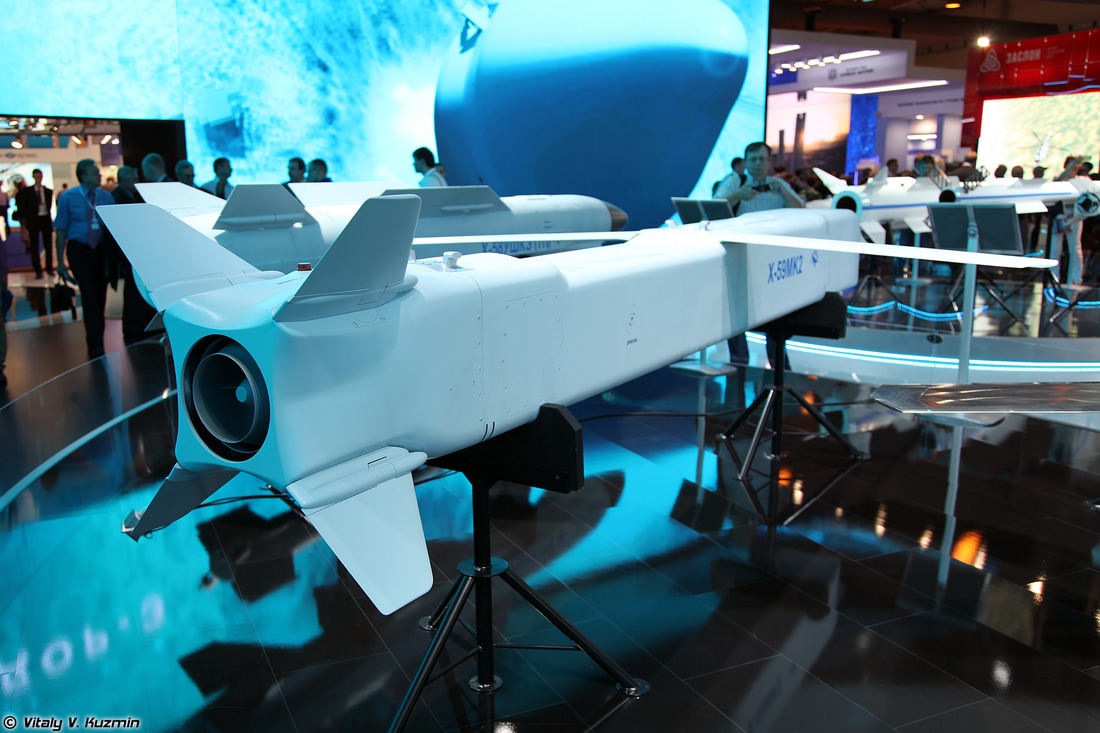
7 Kh-59MK2
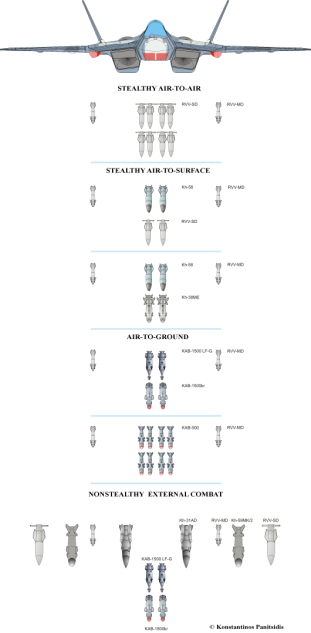
The Kh-59MK2 cruise missile bears little external resemblance to the earlier Kh-59 (AS-18 Kazoo), which is a conventional glide bomb with an externally mounted Saturn 36MT turbofan engine, but uses the same powerplant, warhead and guidance system. It has a redesigned airframe to reduce its radar signature and fit in the Sukhoi T-50’s weapon bays. The 1,700-lb. weapon has a design range of up to 160 nm.
The Kh-59MK2 features a stealth-contoured nose with short, swept horizontal chines, which avoids a radar cross-section (RCS) spike from a rounded nose but takes up less space in the length-limited (4.2-meter-long) T-50 bays than a pointed or wedge nose. Flat sides result in strong RCS spikes at 90-deg. to the missile’s axis, but if the weapon is at low altitude these are not exploitable by an airborne radar, because a radar at that position cannot detect any Doppler signal from the missile. The flush inlet is located under the body.
A third, modified weapon was the Kh-58UShKE-IIR (imaging infrared). The basic Kh-58UShKE, seen at previous MAKS shows, is a modernized, shortened, folding-wing version of the veteran Mach 4 Kh-58 (AS-11 Kilter). The new model adds two IIR sensors under the forebody, allowing the weapon to engage emitters that have been shut down.
The new weapons underscore the fact that the T-50 cannot be regarded as an analog to the Lockheed Martin F-22. It is designed for both air-to-air and air-to-surface missions, with the ability to carry four large weapons internally (versus two 1,000-lb. bombs on the F-22) as well as having provision for Kh-31 anti-radar missiles under the wings.
Anti-Ship Missile.
KH 35
Kh-35UE (AS-20 “Kayak”) anti-ship missile
Kh-35UE (AS-20 “Kayak”) anti-ship missile (wings extended)
The Zvezda Kh-35U (‘Star’, Russian: Х-35У, AS-20 ‘Kayak’) is the jet-launched version of a Russian subsonic anti-ship missile. The same missile can also be launched from helicopters, surface ships and coastal defence batteries with the help of a rocket booster, in which case it is known as Uran (‘Uranus’, SS-N-25 ‘Switchblade’, GRAU 3M24 ) or Bal (‘Ball’, SSC-6 ‘Sennight’, GRAU 3K60). It is also nicknamed “Harpoonski”, because it looks like and functions very similar to the American Harpoon Anti-Ship missile. It is designed to attack vessels up to 5000 tonnes.
The Kh-35 missile is a subsonic weapon featuring a normal aerodynamic configuration with cruciform wings and fins and a semisubmerged air duct intake. The propulsion unit is a turbofan engine. The missile is guided to its target at the final leg of the trajectory by commands fed from the active radar homing head and the radio altimeter.
Target designation data can be introduced into the missile from the launch aircraft or ship or external sources. Flight mission data is inserted into the missile control system after input of target coordinates. An inertial system controls the missile in flight, stabilizes it at an assigned altitude and brings it to a target location area. At a certain target range, the homing head is switched on to search for, lock on and track the target. The inertial control system then turns the missile toward the target and changes its flight altitude to an extremely low one. At this altitude, the missile continues the process of homing by the data fed from the homing head and the inertial control system until a hit is obtained.
The Kh-35 anti-ship missile can be employed in fair and adverse weather conditions at sea states up to 5-6, by day and night, under enemy fire and electronic countermeasures.
The Kh-35’s aerodynamic configuration is optimized for high subsonic-speed sea-skimming flight to ensure stealthy characteristics of the missile. The missile has low signatures thanks to its small dimensions, sea-skimming capability and a special guidance algorithm ensuring highly secure operational modes of the active radar seeker.
Its ARGS-35E active radar seeker operates in both single-and-multiple missile launch modes, acquiring and locking on targets at a maximum range of up to 20 km. A new radar seeker, Gran-KE have been developed by SPE Radar MMS and will be replacing the existing ARGS-35E X band seeker.
Weapon Configurations Of PAK-FA