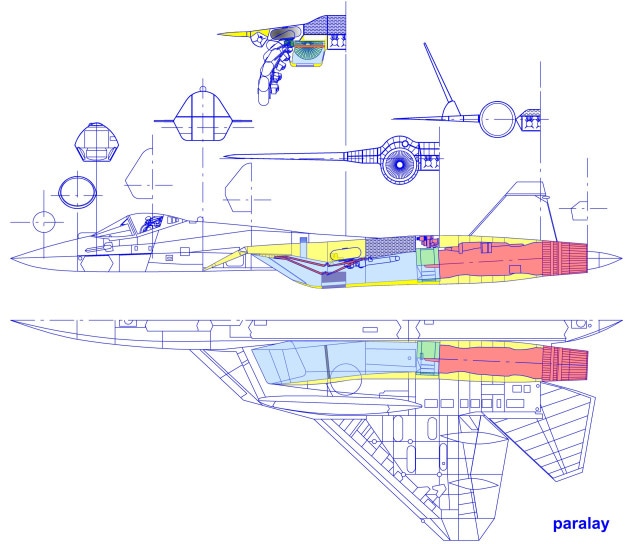
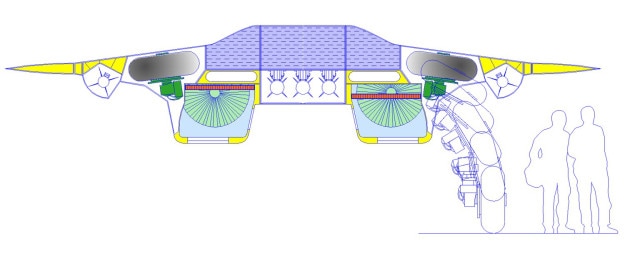
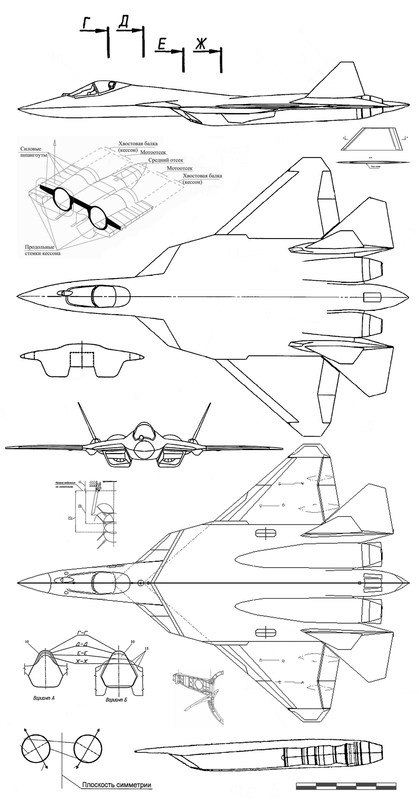
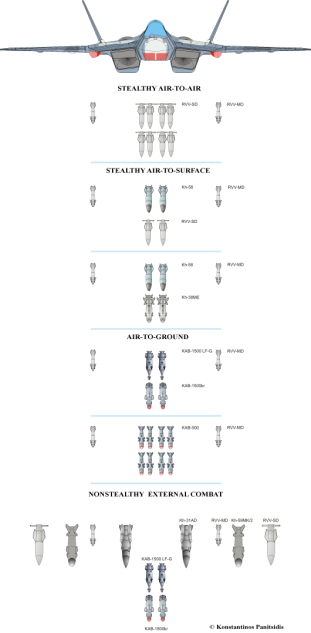
Air to Air weapons
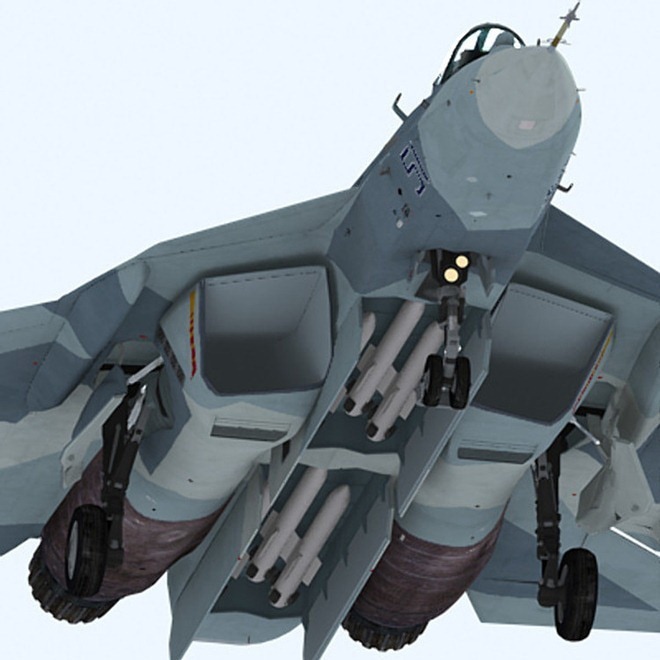
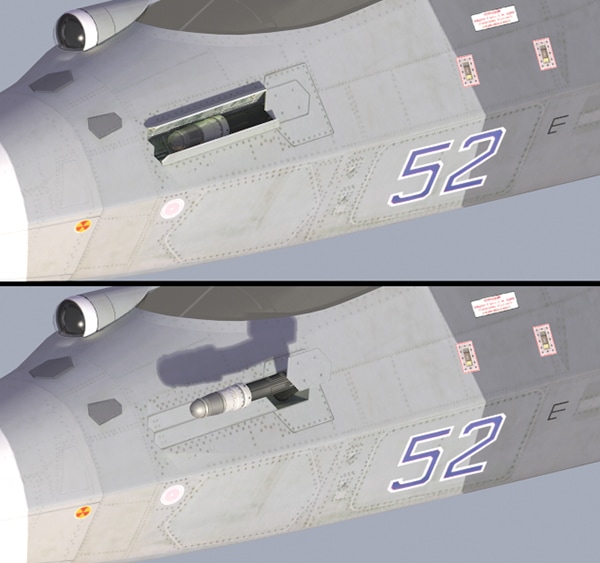
T 50 already has a large number of choices for air to air missiles of all types. But being a next generation aircraft. New missiles are being developed. These new missiles must have significant resistance to jamming and should get least confused by flares. They should also have reduced cross section in an order to be fitted inside the restricted size of the weapon bays of PAK-FA. The two central weapon bays are designed to carry six mid range and four long range AAMs.
1. K-77M (izdeliye 180)
It is a Medium-range missile having active radar-homing K-77M (izdeliye 180), an upgraded R-77 variant with AESA seeker and conventional rear fins
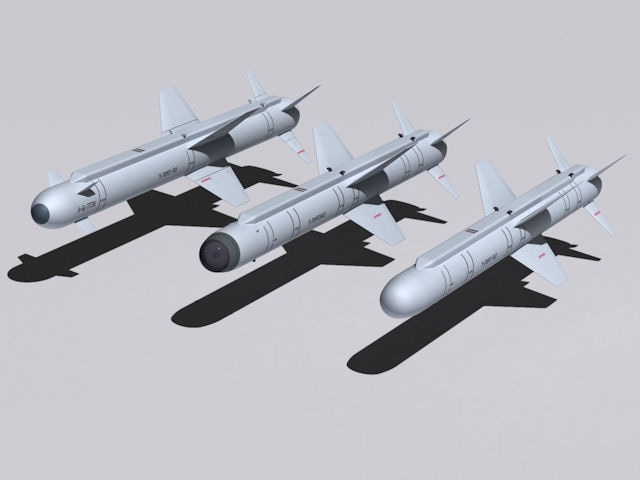
The Vympel NPO R-77 missile (NATO reporting name: AA-12 Adder) is a Russian medium range, active radar homing air-to-air missile system. It is also known by its export model designation RVV-AE. It is the Russian counterpart to the American AIM-120 AMRAAM missile.
Another improvement program was designated the R-77M, which made the missile longer and heavier, making use of a two-stage motor as well as an improved seeker. A further product-improvement of the R-77, designated the R-77M1 and then the R-77-PD, was to feature a ramjet propulsion device. This missile was destined for the MiG 1.44 that for the MFI program. The weapon has a laser fuse and an expanding rod warhead that can destroy the variable sized targets.
According to specifications, the R-77-1 and its export variant RVV-SD is 15 kg (33 lb) heavier than the basic R-77 / RVV-AE, weighing 190 kg (420 lb) rather than 175 kg (386 lb). Maximum range is increased to 110 km (68 mi) from 80 km (50 mi). The missile is also slightly longer at 3.71 metres (12.2 ft), rather than the 3.6 metres (11.8 ft) of the basic variant. Additional improvements include upgrades to the missile’s radar seeker and boat tail rear section to reduce drag.
Russian missile manufacturer Agat previously confirmed it was working on seeker upgrades for the R-77, implying that at least two projects were underway, one for export and one for the Russian air force.
2. K-74M2 (izdeliye 760)
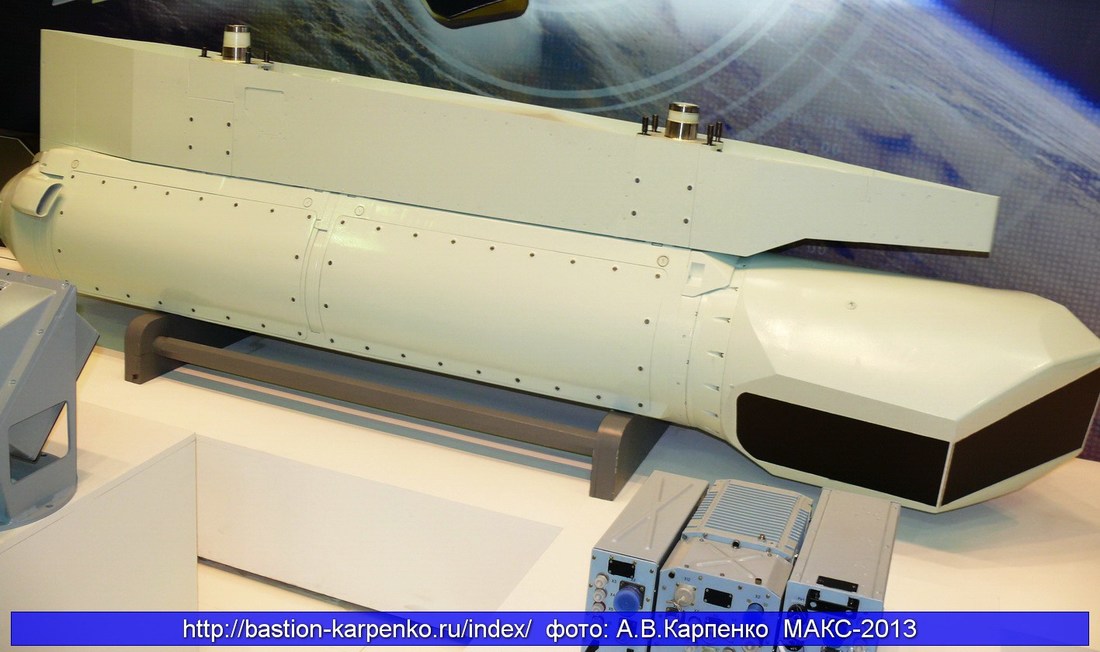
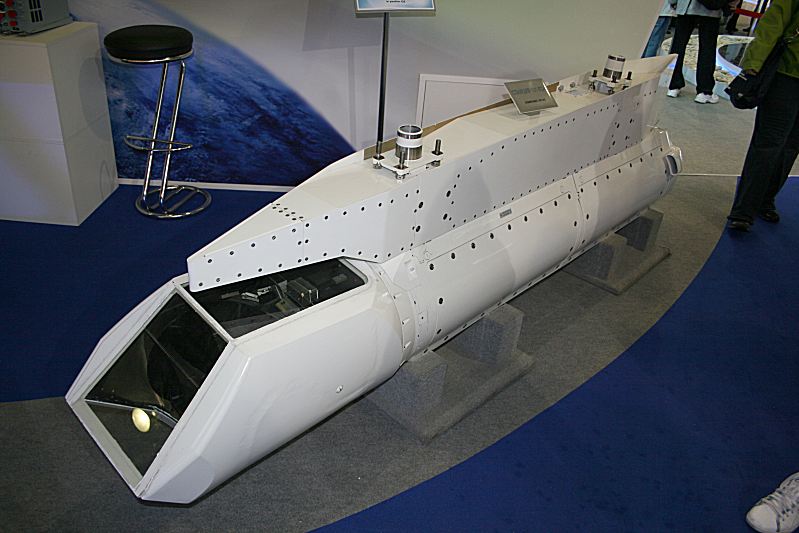
It is the infrared-homing (“heat seeking”) short range missile. K-74M2 (izdeliye 760), an upgraded R-74 variant with reduced cross-section for internal carriage. For the PAK FA, Vympel is developing two new missiles based on R-73/R-74 technology. The first of these is izdeliye 760. Based on the K-74M, this is intended to match the performance of the MBDA Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM) and the Raytheon AIM-9X Sidewinder. It will have an improved IR seeker, an inertial control system, a datalink receiver for target updates and an advanced rocket motor with a longer burn time. To make the missile suitable for internal carriage, its cross-section will be reduced to 320×320 mm.
To maximise the weapon’s coverage, it can be fired in lock-on-after-launch (LOAL) mode, starting under inertial control before achieving in-flight lock-on. It will be able to engage targets up to 160° from the aircraft’s heading.
The follow-on K-MD (izdeliye 300) is intended to outperform the ASRAAM and AIM-9X. Although it will draw on the experience gained with the R-73/R-74 series, for most practical purposes it will be an all-new missile.
Its guidance system will be based on a new IR seeker incorporating a focal-plane array (FPA). This will have more than twice the lock-on range of the izdeliye 760 seeker, a high resistance to countermeasures and a target-recognition capability.
Air To Ground weapons.
The air to ground weapons for T 50 would be mostly the improved versions of previous Russian air to surface missiles. But some of them are said to be optimised with square cross section for proper fitting and have improved performance.
1.
Kh-38M air-to-ground missiles
Kh-38 is a family of highly modular air to surface missiles. Kh-38ME family consists of the following missiles: Kh-38MAE, Kh-38MKE, Kh-38MLE and Kh-38MTE modular aircraft guided missiles designed to shoot down a broad range of armored, reinforced and soft ground targets, sea surface and coastal targets, as well as groups of targets.
The Kh-38ME series is a comprehensive battlefield weapon, also launched from positions in tactical depth. Modularity brings high combat effectiveness against a variety of targets owing to the use of different payloads and guidance methods:
– Kh-38MAE – inertial + active radar guidance;
– Kh-38MKE – inertial + satellite guidance;
– Kh-38MLE – inertial + semiactive laser guidance;
– Kh-38MTE – inertial + thermal-imaging guidance.
The 250-kg payload (half of the missile total weght) consists of HE-Frag or penetrating warhead in Kh-38MAE, Kh-38MLE and Kh-38MTE, or a cluster warhead in Kh-38MKE.
The two-phase solid-propellant motor allows the missile to attain a speed twice as high as the speed of a sound. Kh-38MEs are carried by both FW and RW aircraft.
Performance:
Launch range in km :- 3 – 40
Launch speed km/h (max Mach number) :- 2.2
Max missile turn angle, degrees in horizontal plane after launch :- (+;-) 80
Target destruction probability under enemy’s attack/without enemy’s attack :- 0.8/0.6
Shelf life :- 10 years.
Warhead weight :- up to 250 KGS.
Fuse type :- contact fuse
Motor :- Two-phase solid-propellant motor
Max launch weight :- 520 kgs
Dimensions LengthxDiameterxWing span :- 4.2 x 0.31 × 1.14 m.
Launch conditions: launch range :- 200 to 1200 m.
speed range 15 to 450 m/sec.
2. Kh-31PD anti-radiation missile
The Kh-31P is based on the normal aerodynamic scheme with X-shaped arrangement of the wing and rudder. The missile consists of three compartments. Each compartment is a structurally and functionally complete unit. In the case in a plane bearing surfaces there are four round side supersonic inlet closed in flight discharged plugs conical shape. The Kh-31P is equipped with high-explosive fragmentation warhead, upgraded X-31PD – universal tape, weighing 110 kg, increased lethality.
Engine 31DPK – ramjet, created in the ICD “Soyuz” (city Turaevo Moscow region). It consists of: air intakes, fuel tanks with a system of repression and fuel metering equipment, front-line unit, the combustion chamber with a fixed supersonic nozzle, electrohydraulic control system roszhiga.
Kh-31P/31PD
Range, km: – Maximum 110 km. , – Minimum :- 15 km.
Flight speed, m / s: – Maximum :- 1000, – Mean :- 600-700.
Airspeed carrier km / h :- 600 -1250.
Height start, km :- 0.1-15.
Dimensions, mm:
– Length :- 4700 mm
– Maximum body diameter :- 360 mm
– Wingspan :- 778 mm
– Swing rudders :- 914 mm
Starting weight, kg :- around 600 to 715
Weight of warhead, kg :- 87-90
Bearing angle goal at the start:
– Takeover target by carrier :- ± 15 °
– A takeover target in the path :- ± 30 °
Developer :- IBC “Vympel”
Empty weight PU, kg :- 185.
3 Korrektiruyemaya Aviatsionnaya Bomba (KAB) family of bombs.
Developed by JSC KABs are a family of precision guided bombs consisting various explosive weights and various guidance systems.
KAB 250
It is having 250 kgs explosives. It has a laser-guided version (the KAB-250LG-E) and the GLONASS/INS-guided KAB-250S-E. Its circular error probable (CEP) for ground targets is 3-5 m.
KAB-500 precision guided bombs
KAB-500Kr CONTROLLED AIR BOMB
Size, kg 500
Weight of warhead , kg 380
Guidance system TV correlation
homing head ensuring target lockon
while aboard the carrier
and automatic guidance during fall
Warhead HE concrete-piercing
Combat use conditions in daytime
at visually discernible targets
during level flight or dive
Guidance accuracy (CEP), m up to 4
KAB-500-OD CONTROLLED AIR BOMB
Size, kg 500
Weight of warhead , kg 250
Guidance system TV correlation
homing head
Warhead fuel-air explosive
Combat use conditions in daytime at visually
discernible targets
during level flight
or dive on the
drop-and-forget principle
Guidance accuracy (CEP), m up to 4
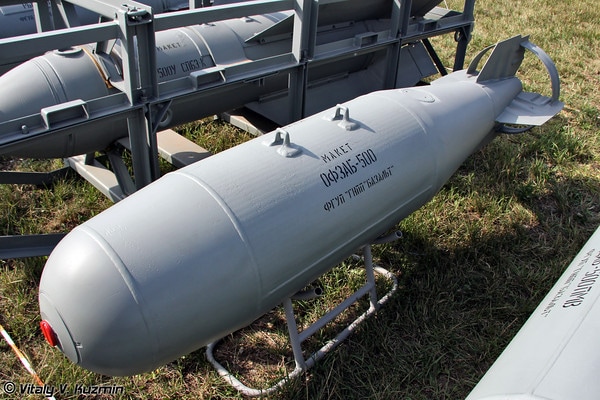
4 OFZAB-500
High-explosive incendiary bomb aviation OFZAB-500 was established use in high speed with low altitudes against manpower and easily vulnerable field installations, warehouses and fuel depots. The bomb is intended to replace in the Russian Air Force obsolete FOZAB-500. It is used at altitudes of 300 – 20,000 m at speeds of 100 – 1200 km / h. OFZAB-500 allows the wearer to carry out maneuvers with large congestion.
Length, m
Diameter, mm
span, m
weight bombs, kg
Weight of explosive, kg 2.5
450
0.5
500
250 kg incendiary + 37.5 kg PF
5 ODAB-500PMV (ОДАБ-500ПМВ – Объемно-детонирующая авиационная бомба) thermobaric air bomb
Bomb manufactured by the Russian company basalts. Furthermore, the term thermobaric air bomb can meet even the names vacuum bomb, fuel, bomb, aerosol bomb, v detonujúca bomb or a high-explosive bomb.
The bomb is designed to control industrial zones, unprotected or protected by live force (eg. In enclosures, tunnels, caves), nepancierovanej technology and military equipment. The bomb is scheduled for troop (front) airplanes and helicopters. It can be used for the destruction of anti-personnel mines and anti-tank.Planes can toss a bomb from a height of 200 to 12,000 m at speeds of 500-1500 km / hr. Helicopters can toss a bomb from a height of 1100 – 4000 M at speeds of 50-300 km / h.
Bomb has built a lighter.
Diameter Bomb: 500 mm
Length: 2380 mm
Weight bombs: 525 kg
Weight of filling: 193 kg
equivalent of TNT explosions: 1000 kg
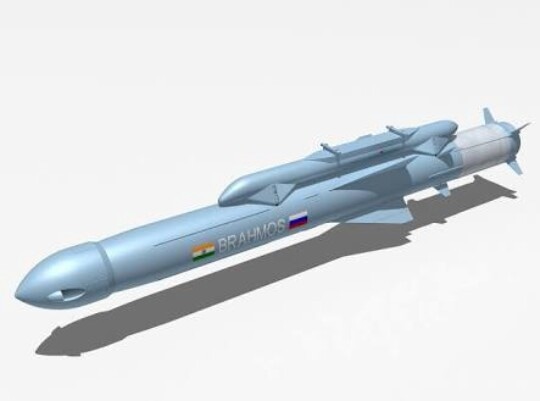
6 BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles.
It is based on the Russian P-800 Oniks cruise missile and other similar sea-skimming Russian cruise missile technology. The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia. It is the world’s fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation. The missile travels at speeds of Mach 2.8 to 3.0
BrahMos-A
The BrahMos-A is a modified air-launched variant of the missile which will arm the Sukhoi PAK-FA of the Indian air force as a standoff weapon. To reduce the missile’s weight to 2.55 tons, many modifications were made like using a smaller booster, adding fins for airborne stability after launch, and relocating the connector. It can be released from the height of 500 to 14,000 meters (1,640 to 46,000 ft). After release, the missile free falls for 100–150 meters, then goes into a cruise phase at 14,000 meters and finally the terminal phase at 15 meters.
BrahMos-NG
BrahMos-NG (Next Generation) is a mini version based on the existing BrahMos, will have same 290 km range and mach 3.5 speed but it will weigh around 1.5 tons, 5 meters in length and 50 cm in diameter, making BrahMos-NG 50 percent lighter and three meters shorter than its predecessor. The system is expected to be inducted in the year 2017. BrahMos-NG will have lesser RCS (radar cross section) compared to its predecessor, making it harder for air defense systems to locate and engage the target. BrahMos-NG will have Land, Air, ship-borne and Submarine tube-launched variants. First test flight is expected to take place in 2017–18. Initially Brahmos-NG was called as Brahmos-M.
BrahMos-II
BrahMos-II is a hypersonic cruise missile currently under development and is estimated to have a range of 290 km. Like the BrahMos, the range of BrahMos II has also been limited to 290 km to comply with the MTCR. With a speed of Mach 7, it will have double the speed of the current BrahMos missile, and it will be the fastest hypersonic missile in the world. Development could take 7–8 years to complete.
7 Kh-59MK2
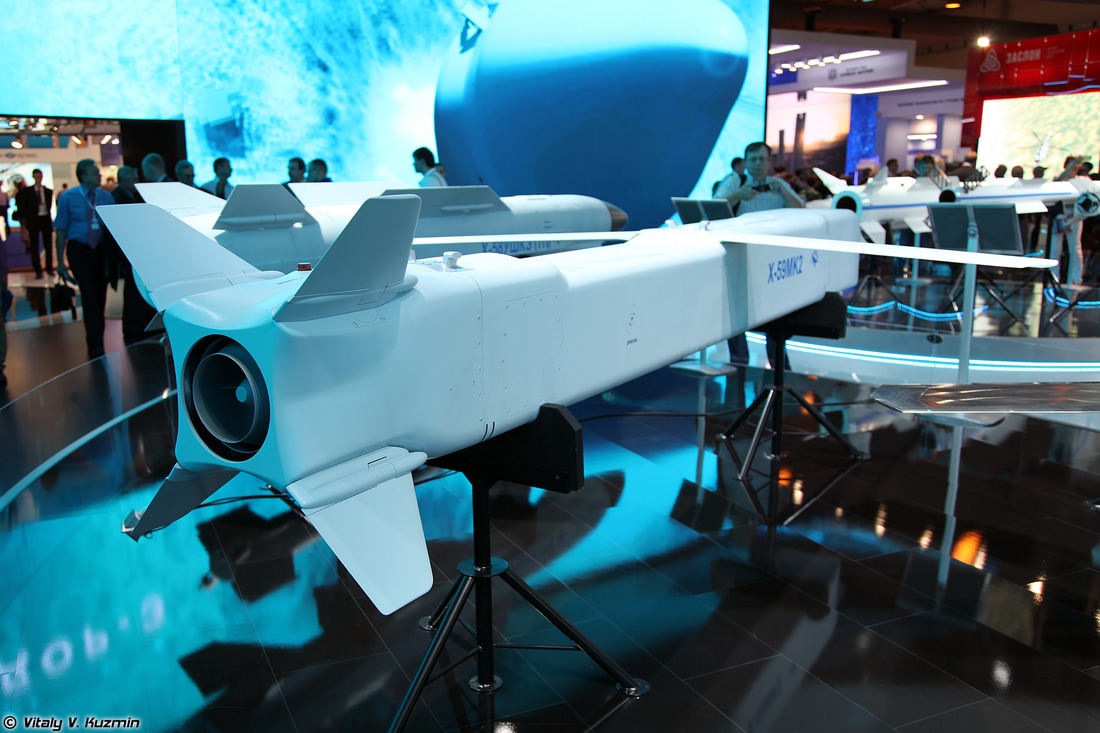
The Kh-59MK2 cruise missile bears little external resemblance to the earlier Kh-59 (AS-18 Kazoo), which is a conventional glide bomb with an externally mounted Saturn 36MT turbofan engine, but uses the same powerplant, warhead and guidance system. It has a redesigned airframe to reduce its radar signature and fit in the Sukhoi T-50’s weapon bays. The 1,700-lb. weapon has a design range of up to 160 nm.
The Kh-59MK2 features a stealth-contoured nose with short, swept horizontal chines, which avoids a radar cross-section (RCS) spike from a rounded nose but takes up less space in the length-limited (4.2-meter-long) T-50 bays than a pointed or wedge nose. Flat sides result in strong RCS spikes at 90-deg. to the missile’s axis, but if the weapon is at low altitude these are not exploitable by an airborne radar, because a radar at that position cannot detect any Doppler signal from the missile. The flush inlet is located under the body.
A third, modified weapon was the Kh-58UShKE-IIR (imaging infrared). The basic Kh-58UShKE, seen at previous MAKS shows, is a modernized, shortened, folding-wing version of the veteran Mach 4 Kh-58 (AS-11 Kilter). The new model adds two IIR sensors under the forebody, allowing the weapon to engage emitters that have been shut down.
The new weapons underscore the fact that the T-50 cannot be regarded as an analog to the Lockheed Martin F-22. It is designed for both air-to-air and air-to-surface missions, with the ability to carry four large weapons internally (versus two 1,000-lb. bombs on the F-22) as well as having provision for Kh-31 anti-radar missiles under the wings.
Anti-Ship Missile.
KH 35
Kh-35UE (AS-20 “Kayak”) anti-ship missile
Kh-35UE (AS-20 “Kayak”) anti-ship missile (wings extended)
The Zvezda Kh-35U (‘Star’, Russian: Х-35У, AS-20 ‘Kayak’) is the jet-launched version of a Russian subsonic anti-ship missile. The same missile can also be launched from helicopters, surface ships and coastal defence batteries with the help of a rocket booster, in which case it is known as Uran (‘Uranus’, SS-N-25 ‘Switchblade’, GRAU 3M24 ) or Bal (‘Ball’, SSC-6 ‘Sennight’, GRAU 3K60). It is also nicknamed “Harpoonski”, because it looks like and functions very similar to the American Harpoon Anti-Ship missile. It is designed to attack vessels up to 5000 tonnes.
The Kh-35 missile is a subsonic weapon featuring a normal aerodynamic configuration with cruciform wings and fins and a semisubmerged air duct intake. The propulsion unit is a turbofan engine. The missile is guided to its target at the final leg of the trajectory by commands fed from the active radar homing head and the radio altimeter.
Target designation data can be introduced into the missile from the launch aircraft or ship or external sources. Flight mission data is inserted into the missile control system after input of target coordinates. An inertial system controls the missile in flight, stabilizes it at an assigned altitude and brings it to a target location area. At a certain target range, the homing head is switched on to search for, lock on and track the target. The inertial control system then turns the missile toward the target and changes its flight altitude to an extremely low one. At this altitude, the missile continues the process of homing by the data fed from the homing head and the inertial control system until a hit is obtained.
The Kh-35 anti-ship missile can be employed in fair and adverse weather conditions at sea states up to 5-6, by day and night, under enemy fire and electronic countermeasures.
The Kh-35’s aerodynamic configuration is optimized for high subsonic-speed sea-skimming flight to ensure stealthy characteristics of the missile. The missile has low signatures thanks to its small dimensions, sea-skimming capability and a special guidance algorithm ensuring highly secure operational modes of the active radar seeker.
Its ARGS-35E active radar seeker operates in both single-and-multiple missile launch modes, acquiring and locking on targets at a maximum range of up to 20 km. A new radar seeker, Gran-KE have been developed by SPE Radar MMS and will be replacing the existing ARGS-35E X band seeker.
Weapon Configurations Of PAK-FA