I think you could be right - story has disappeared from the site.Progressing well , but no info about engine , mission computer , i think they miced info of tfx and hurjet ,as hurjet may come by 2023 , tfx is next to impossible by 2023
AMCA - Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (HAL)
- Thread starter screwterrorists
- Start date
More options
Who Replied?- Joined
- Jan 26, 2021
- Messages
- 7,365
- Likes
- 27,771
Wait for some time ,before it is deferred to 2035 , even turkish media , their defense analyst are not so confident on it , these press release and all are misinterpreted many times ,in india too .I think you could be right - story has disappeared from the site.
They tried to sell it hard in paris show , to garmer any supporting nation from nato ,but all are interested in fcas or tempest , developer of latter two are far more experienced ,and are involved in f 35 program more than just some airframe parts manufacturing like turks
MirageBlue
New Member
- Joined
- Mar 19, 2020
- Messages
- 669
- Likes
- 3,723
Our politicians and bureaucrats in many instances were penny wise pound foolish as they didn't get the long term consequences of their decisions. That decision not to finance the upgraded engine was one such.OK. DIY. Or do it with SAFRAN.
By the way, RR offered to increase the thrust of the Orpheus from 4,900 lbs thrust for not a lot (reportedly £3 million) but GOI did not want to finance it. Instead India went for the Brandner E-300 engine being developed to power the Egyptian Helwan HA-300. So which party was not flexible? India was offered a more powerful engine by RR. India chose another route. Unfortunately HA-300 was cancelled, along with its engine in 1969.
The Jaguar re-engining program also went that way..RR offered to upgrade the existing Adour engine on the Jaguar but the IAF chose the riskier option that Honeywell offered and eventually it got so expensive that the entire re-engining program died.
- Joined
- Jun 6, 2021
- Messages
- 722
- Likes
- 1,132
The transonic trap refers to a phenomenon in which the SU-27's stable coil envelope can be used to plummet during the transonic phase.Never heard of it for Su30MKI
.
The transonic structure limit of 6.5G also appeared in the manual.
The essence of the transonic trap is the forward movement of the center of pressure caused by the deceleration of the transonic maneuver and the loss of lift after the center of gravity caused by the shock wave stall, which causes a sudden change in the aircraft's pitch load.
I use the translation software to translate some academic terms, I don’t know if it’s right
- Joined
- Jun 6, 2021
- Messages
- 722
- Likes
- 1,132
This is explained in "AIAA 2004-4752 Asymmetric Stiffness Feedback Control-EF-2000 Transonic Lifting Mitigation"Never heard of it for Su30MKI
On aircraft with swept-back wings, the centre of pressure is more aft for supersonic Mach numbers than for subsonic Mach numbers. Consequently, it moves forward when the aircraft decelerates from super- to subsonics, thereby generating a nose-up (positive) pitching moment. In addition, at certain combinations of (transonic) Machnumber and angle of attack, flow separation occurs on the outboard wing and destroys lift behing the c.g. thereby generating a violent pitch-up transient. Both effects together generate uncommanded vertical load factor transients that jeopardize the flying qualities of the aircraft, threaten the pilot's health and lead to violations of the aircraft's structural load limits.
A transonic pitch-up problem is present on many fighter aircraft and various measures intended to control the flow-breakdown on the upper surface of wings with swept leading-edges are known. Fences, notches, saw-cuts, sawteeth, trips, Gurney-flaps, and vortex generators are examples of aerodynamic measures installed on existing fighter aircraft. Whereas a certain limited pitch-up mitigation can be expected from such measures, no single measure solving the phenomenon completely is known.
From the above text, everyone has clearly found that the transonic aircraft faces two problems. One is the forward movement of the center of pressure caused by maneuvering deceleration.
To put it simply, the transonic trap is like a roller coaster ride. You obviously made a 6G overload, but you impose an 11G overload, and this kind of overload overload is non-linear.
The transonic trap is a phenomenon in which a transonic vertical overload is out of control. It is very dangerous for any transonic maneuvering aircraft and crew.
- Joined
- Jun 6, 2021
- Messages
- 722
- Likes
- 1,132
How to solve the transonic trap
United States
F-15
There is a system like OWS
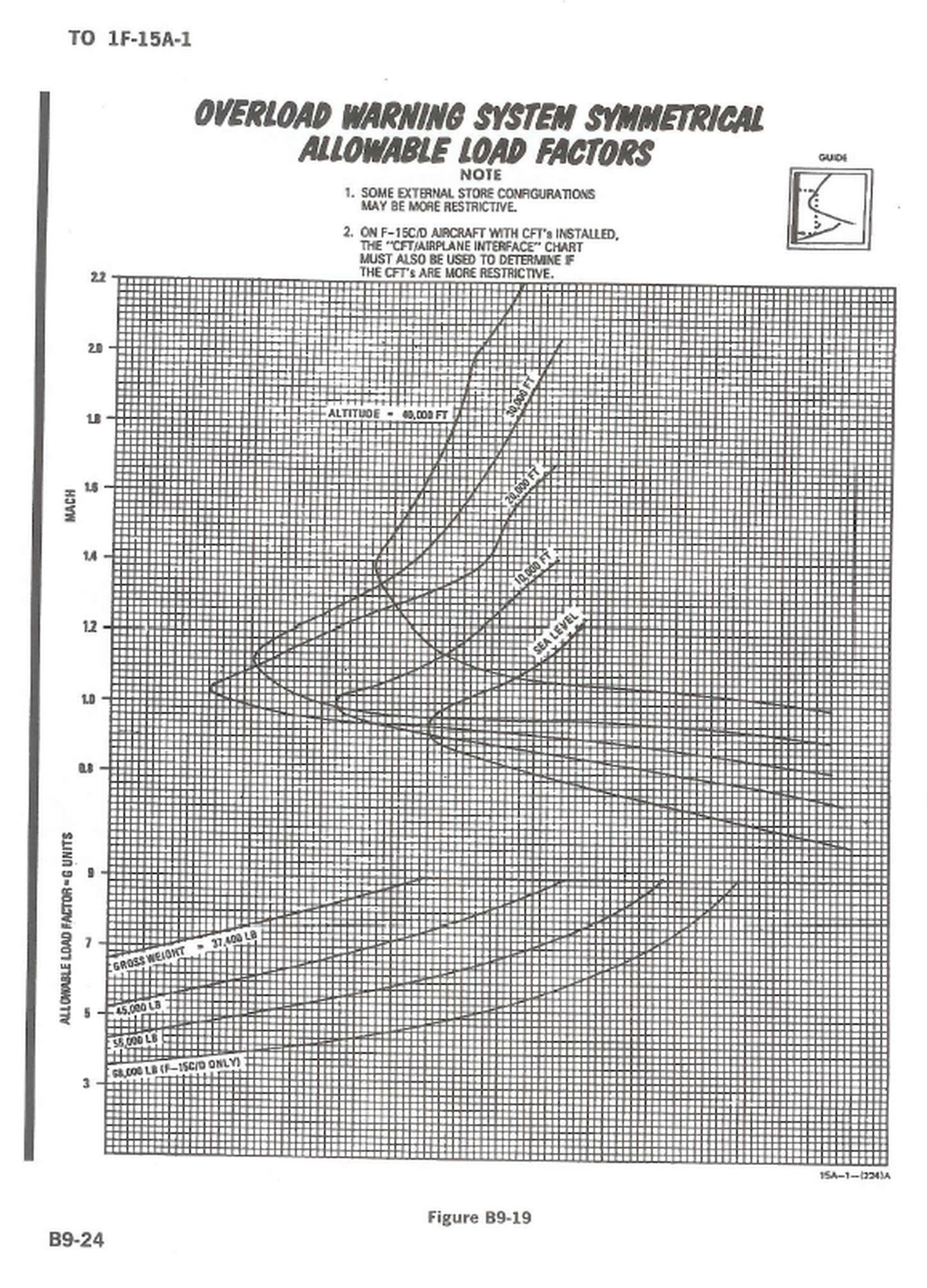
It can be seen that even the lightest 34,000 pounds, the available overload at 10,000 feet transonic speed will deteriorate.
If you can say that the above is only the system limit can be surpassed at any time
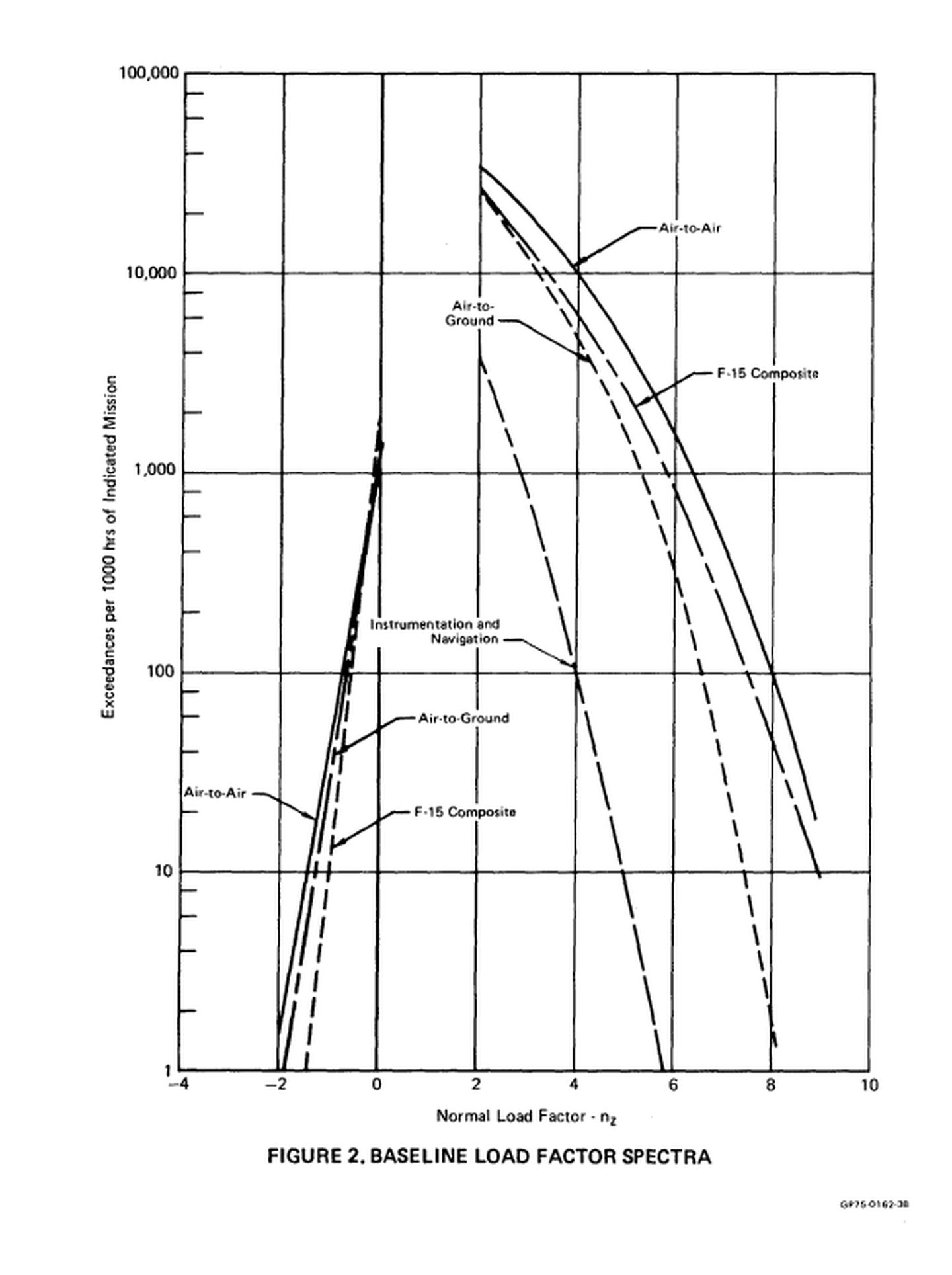
This is the F-15 load spectrum in 1977. It can be seen that the available overload requirement per 1,000 flight hours is quite strict.
F-18E/F
The FA18 manual describes the overload limiter like this
Additionally, during elevated-g maneuvering at transonic flight conditions, the g-limiter unloads the aircraft (and NzREF) by as much as 1.0 to 1.7g. This feature helps prevent an aircraft overstress that could result from the classic aerodynamic phenomenon known as ”transonic pitch-up“ experienced during elevated-g decelerations at transonic flight conditions.
In addition, when performing high-overload maneuvers under transonic flight conditions, the overload limiter will reduce the aircraft's overload by 1.0 to 1.7G. This function helps prevent the classic aerodynamics that occur when the overload is increased under transonic flight conditions. Aircraft overload caused by the phenomenon "transonic pitch up".
EF-2000
The aforementioned AIAA 2004-4752 wrote:
Finally, flight test results are presented. The solution implemented reduces the pitch-up transient to 1.5 g and constrains the maximum vertical load factor to respect the structural load limits.
PS: Most of the focus of this article is on the improvement of the EF-2000 flight control law. I have a very little understanding of automatic control, so I can’t give you a more in-depth interpretation.
United States
F-15
There is a system like OWS
It can be seen that even the lightest 34,000 pounds, the available overload at 10,000 feet transonic speed will deteriorate.
If you can say that the above is only the system limit can be surpassed at any time
This is the F-15 load spectrum in 1977. It can be seen that the available overload requirement per 1,000 flight hours is quite strict.
F-18E/F
The FA18 manual describes the overload limiter like this
Additionally, during elevated-g maneuvering at transonic flight conditions, the g-limiter unloads the aircraft (and NzREF) by as much as 1.0 to 1.7g. This feature helps prevent an aircraft overstress that could result from the classic aerodynamic phenomenon known as ”transonic pitch-up“ experienced during elevated-g decelerations at transonic flight conditions.
In addition, when performing high-overload maneuvers under transonic flight conditions, the overload limiter will reduce the aircraft's overload by 1.0 to 1.7G. This function helps prevent the classic aerodynamics that occur when the overload is increased under transonic flight conditions. Aircraft overload caused by the phenomenon "transonic pitch up".
EF-2000
The aforementioned AIAA 2004-4752 wrote:
Finally, flight test results are presented. The solution implemented reduces the pitch-up transient to 1.5 g and constrains the maximum vertical load factor to respect the structural load limits.
PS: Most of the focus of this article is on the improvement of the EF-2000 flight control law. I have a very little understanding of automatic control, so I can’t give you a more in-depth interpretation.
Pash
New Member
- Joined
- Oct 21, 2016
- Messages
- 1,849
- Likes
- 9,133
Turkish Aerospace Begins Building Wind Tunnel For Fighter Program | Aviation Week Network
Turkish Aerospace (TAI) has begun constructing a wind tunnel to support development of Turkey’s planned indigenous combat aircraft, TF-X.
Spotted this from February regarding possible DRDO/RR 116kN engine.
PS The report says that the feasibility study should be concluded near end 2021/start 2022. So a 'no go' decision is possible by year end. A 'yes go' might take a lot longer, I guess.
PS The report says that the feasibility study should be concluded near end 2021/start 2022. So a 'no go' decision is possible by year end. A 'yes go' might take a lot longer, I guess.
Last edited:
Kalkioftoday
New Member
- Joined
- Nov 20, 2020
- Messages
- 327
- Likes
- 1,838
They still need a supersonic wind tunnel for testing.Turkish Aerospace Begins Building Wind Tunnel For Fighter Program | Aviation Week Network
Turkish Aerospace (TAI) has begun constructing a wind tunnel to support development of Turkey’s planned indigenous combat aircraft, TF-X.aviationweek.com
- Joined
- Jan 14, 2020
- Messages
- 9,609
- Likes
- 84,139
It's transonic tunnel enough for testing aircraft.They still need a supersonic wind tunnel for testing.
- Joined
- Oct 14, 2020
- Messages
- 28,260
- Likes
- 195,943
- Joined
- Jan 26, 2021
- Messages
- 7,365
- Likes
- 27,771
Wrong thread
SUPERPOWER
New Member
- Joined
- Oct 2, 2020
- Messages
- 1,488
- Likes
- 5,302
Looks Like VTOL.
- Joined
- Oct 14, 2020
- Messages
- 28,260
- Likes
- 195,943
Look at the canopy
 .
.Vinod DX9
New Member
- Joined
- Apr 4, 2017
- Messages
- 1,356
- Likes
- 4,410
It's ok,need for further discussion on AMCA.Wrong thread
Vinod DX9
New Member
- Joined
- Apr 4, 2017
- Messages
- 1,356
- Likes
- 4,410
I think there will be a naval variant as well. VTOL or STOBAR....but STOBAR will have only limited customer. India specifically. So unlikely. VTOL might draw Turkey as well. But that too is odd. So naval variant still a doubt.Looks Like VTOL.
- Joined
- Oct 14, 2020
- Messages
- 28,260
- Likes
- 195,943
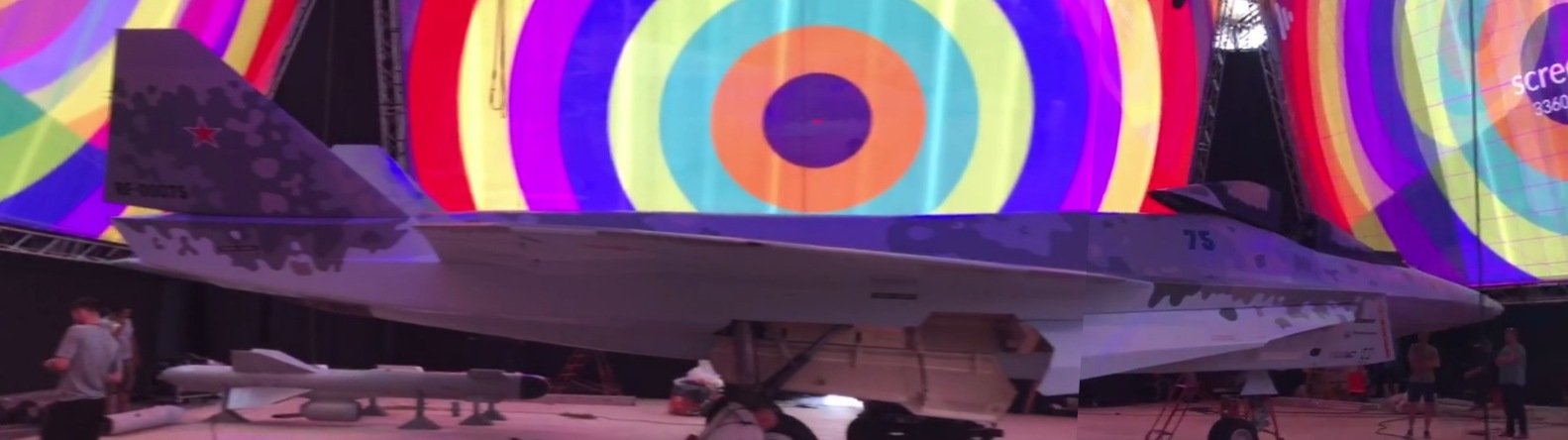
From another angleThis is how new stealth fighter aircraft of Russia might look like..

Articles
-
India Strikes Back: Operation Snow Leopard - Part 1
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 9
-
Aftermath Galwan : Who holds the fort ?
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 33
-
The Terrible Cost of Presidential Racism(Nixon & Kissinger towards India).
- ezsasa
- Replies: 40
-
Modern BVR Air Combat - Part 2
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 22
-
Civil & Military Bureaucracy and related discussions
- daya
- Replies: 32