StealthFlanker
New Member
- Joined
- Aug 12, 2016
- Messages
- 879
- Likes
- 1,213
It kinda funny how people put some science sounding words together with a bunch of nonsense assumption then call it basic physic , here are some mistake in that link just to name a few :The hard facts are that F-22A will never reach supporters expectations due to basic physics – that have nothing to do with program cost(s). – Posted 14-Jan 2014 @theboresight.blogspot.com
1) the author comparing an SR-71 flying at mach 3 with an F-22 flying at mach 1.7 ??? what kind of stupid comparison is that???? the temperature will be extremely different

2) while what he said about aerodynamic heating is correct ( yes they exist ) what he talk about aircraft unable to hide is completely wrong , there are load of stuff that will absorb infrared radiation , cloud is an example
. Moreover , passive sensor such as Infrared sensor lack capabilities to measures range and velocity by themselves and have to rely on LRF to generate firing solution , LRF has very short range , for example the one on OLS-35 can reach merely 20 km
3) and then there is this nonsense :
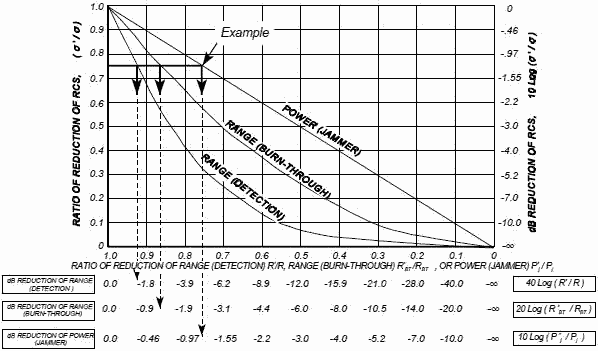
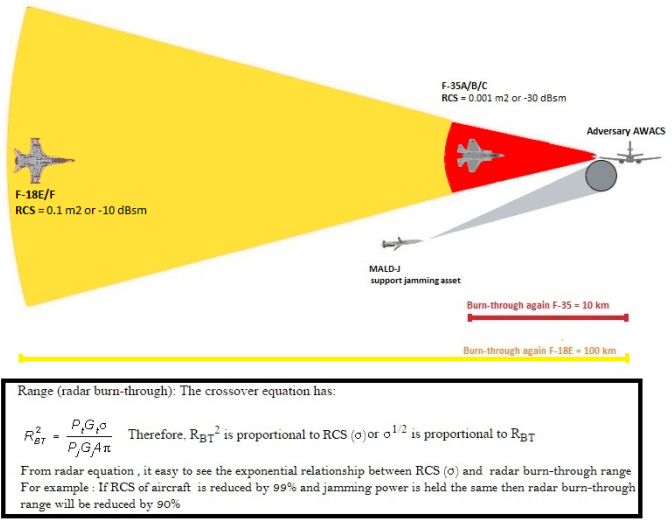
Radar cross section is the measure of a target’s ability to reflect radar signals in the direction of the radar receiver. In others words, it is a measure of the ratio of backscatter power per steradian (unit solid angle) in the direction of the radar (from the target) to the power density that is intercepted by the target , it has nothing to do with the radar time on target, increasing dwell time ( related to pulse length ) will increase the power of the reflection but the trade of is the range resolution will be horrendously badTarget RCS (Radar Cross Section) [below] is determined by 1) the power transmitted in the direction of the target. 2) The amount of power that impacts the target and is reflected back in the direction of the radar. 3) The amount of reflected power that is intercepted by the radar antenna. 4) The length of time in which the radar is pointed at the target.

Moreover ,while high PRF can also improve capability of radar to detect target with low RCS, for unambiguous range measurements, no more than one pulse should be received from the target for each pulse transmitted by the radar. So there is a limit to how high PRF you could go. And the maximum detection range performance value that you often see is already taken in velocity search ( maximum PRF possible ) , so no more range improvement here.
4) then this
The weapon then dives down (using kinetic energy) to kill the target. The target profile presented to the AIM-54 is - the top of the target - not head-on. The top (stealthy or otherwise) provides the largestpossible target: surface area, physical size, and RCS aspect. F-14D (Infrared+radar) targeting in this way, with Phoenix alone - would have presented an unacceptable DACT (Dissimilar Air Combat Training) hazard for the new USAF F-22 Raptor.
firstly , all BVR missiles use a ballistic arc and lead intercept to extend range , AIM-54 isnt the only one
secondly , even though missiles can climb to higher altitude , the angular seperation is really insignificant , especially at long range. Moreover , how can the F-14 get the firing solution in the first place ? AAS-42 doesnt have a LRF device , and good luck lock on the F-22 with the APG-71 really.
5)
i find it ridiculous that the author cant understand that size is a big factor in detectionF-22A 'Pitot' tube is clearly visible at the nose. The Raptor has one tube on either side. These air measurement devices are electrically heated to ~ 270 C (520 F) to keep them from icing at altitude. Indeed, they appear as two hot spots on the nose under FLIR
6)
To create such model you will need to know the exact speed altitude of target , and the exact atmospheric condition of that day ,as soon as the target doesnt fly at a fixed speed , altitude and the attmospheric condition change alittle bit then the accuracy for your guesstimate go out of windowThe IRST might also use its own stored 'Atmospheric Propagation Model' to effectively “make an educated guess” as to target(s) relative range, aspect, and velocity – without the radar or laser rangefinder. In effect, the sensors own performance is characterized to construct a sensitivity model against known objects at known distances and velocities. Then during wartime when IRST sees something - it compares its own “known” internal Atmospheric Propagation Model - and the weapons system then extrapolates target range and bearing.
7)
I dont think author understand the different between visual light , infrared light and common radio frequency used in radar .While they are all electromagnetic wave in principal , their frequency are extremely different , infrared radiation for example has much much higher frequency ( shorter wavelength ) compared to radio frequency , so the doppler effect on them are much harder to observed , you pretty much need astronomical speed to be able to see the effect . Moreover, the reason why doppler effect can be used by radar to determine aircraft speed is because the radar know exact frequency that it transmitted. On the otherhand , you cant know the exact frequency of the infrared radiation that was radiated from adversary aircraft,because this frequency will change along with aircraft speed , altitude , moitures , ambient temperature ..etc none of these are constant , and not to mention the fact that the change is extremely small , you can see how impractical it is to use red/blue shift on IRST , they dont just put LRF on thermal system for fun.John C. Mather, Senior Astrophysicist at the Goddard Space Flight Center, Mars Society, University of Maryland 31-July, 2009; during his remarks on Doppler (red/blue) shift detection resolution-granularity in discussing astrophysics of celestial objects: “…we are able to see the velocity of a star down to one (1) meter per second.”
Advanced Flanker IRST Doppler-shift sensitivity will not require the granularity of astrophysics because an F-22 Raptor traveling at Mach 1.1 will be moving at approximately 374 meters per second. By including air combat closure rates - this figure is even higher (!)
This would seem to fall well within, the definition of militarily useful sensitivity?
8)
So basically he want to launch a missiles with out getting firing solution ( no target altitude , no aspect angle , no velocity , no distance to target , no loft angle ) , yep , say good bye to lead intercept and ballistics arcs , and good luck hiting anything from BVR with that method.Conceptually one can act on a - 'False-Positive' - even if stealth is 100% effective in the radio spectrum:
a) IRST picks something up.
b) Point your radar at it.
c) No (or strange) radar return? = stealth.
d) We don't have stealth.
e) Select R-27T-R-77 class IR weapon - 'Fox!’











 . Just one question......... Hasn't Su-47 has been shelved as TD? Or is the project still alive??
. Just one question......... Hasn't Su-47 has been shelved as TD? Or is the project still alive??