Bhartiya Sainik
New Member
- Joined
- Dec 14, 2021
- Messages
- 457
- Likes
- 1,224
Oh! look! Chinese media reported that they signed friendship treaty with USA & flew side by side 
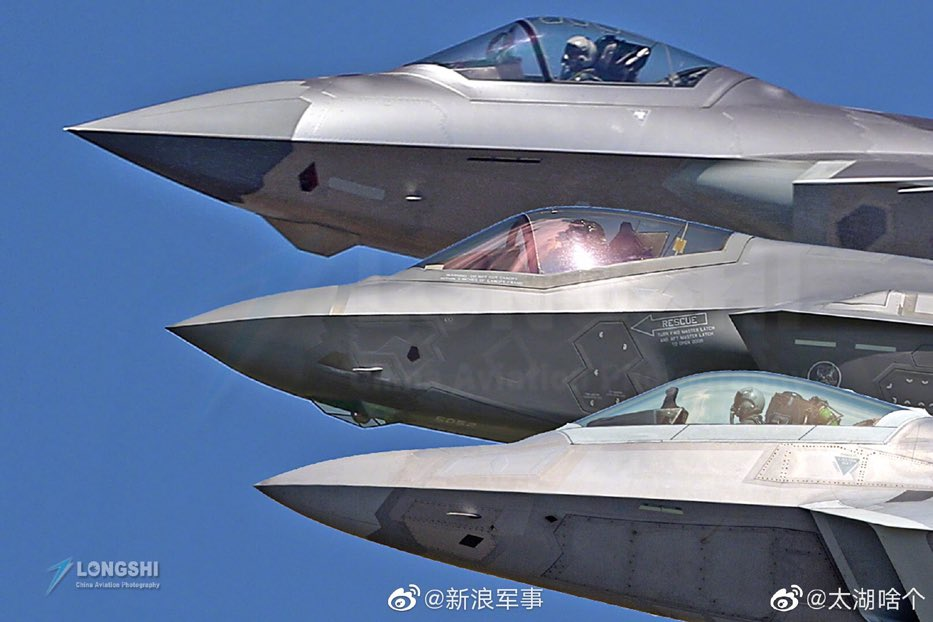
















YYYYAAAAWWWWNNNN!!!!Amid Russian aggression, Fort Worth leaders say the F-35 fighter jet’s value is now on display in Europe
Abby LivingstonMarch 28, 2022
Source- Texas Tribune

WASHINGTON — In the storied history of the factory known as Air Force Plant 4 on Fort Worth’s western edge, there has never been a fighter jet to roll off the assembly line quite like the F-35: It’s an aeronautical marvel, a fiscal disaster and a North Texas economic linchpin.
Military budget hawks call its development a “boondoggle” and a financial “rathole” and floated the idea of scrapping it. Fort Worth lawmakers have steadfastly defended it, touting its value both to the military and the local economy.
But as Western countries scramble to counter Russian aggression in Ukraine,the pride of Fort Worth — Lockheed Martin’s F-35 — is now at the center of American diplomacy and in demand all over Europe. For those who have fought for the program, it’s a validation of that work.
“What’s happening at the plant matters right now,” said Democratic U.S. Rep. Marc Veasey, who grew up underneath the screeching planes of Fort Worth during the twilight of the Cold War. “It seems like that we’re back in that same sort of mindset, that same sort of posture now, because it’s just as serious now, if not more serious than, quite honestly, back then.”
There is almost no conceivable scenario in which the United States would give the Ukrainian military an F-35, according to interviews with several defense policymakers and observers. It’s not even remotely a topic of open discussion because such an action would likely escalate the Ukrainian conflict and pilots would have to be trained on the complex aircraft.
Even so, the F-35 is having an indirect impact in Europe, as countries reconsider their defense readiness in the wake of Russia’s aggression.
Beginning earlier this year, western officials publicized eastward F-35 deployments into and around Europe, announced via tweets, press releases and confirmed news reports. There is likely more classified F-35 activity, and aviation experts regularly track online other F-35 sightings in Eastern Europe.
Get the latest coverage from our Washington bureau, delivered weekly
Sign up here
What is known in published news reports is that American F-35s have migrated to Europe. And Western European countries are deploying their own F-35s into allied countries and airspace in proximity to Russia, in places like Bulgaria, Estonia, Lithuania and Romania. Some are American military planes and others are owned by allies, like the Netherlands.
Aaron Stein, the director of research at the Foreign Policy Research Institute, told The Texas Tribune that American F-35 European air patrols offer “reassurance to the eastern [NATO] members, a symbol of U.S. support for the alliance and also as a signal to the Russians to stay out.”
Other allies are on buying binges of a fighter jet with a price tag in the ballpark of $100 million.
Just prior to the invasion, Finland formalized the purchase of 64 F-35s on Feb. 4, that country’s largest military procurement ever. Earlier this month, American military officials welcomed Finnish Minister of Defence Antti Kaikkonen for a tour of a Florida F-35 training facility, an occasion military officials detailed in a news release. Finland is not a member of NATO.
Most dramatically, German leaders announced three weeks after the Russian invasion their own purchase of 35 F-35 jets. Germany has had a historical reluctance to engage in a military build-up after the horrors of World War II, and that announcement was part of a major shift in policy.
And on Monday, the Canadian government announced that it would buy 88 of the fighter jets, a purchase for which it has reportedly budgeted about $15 billion. These fresh foreign purchases will help offset recent announcements from American military leaders about cutsto their own F-35 orders.
An economic boon
The F-35 is manufactured in several places, but Air Force Plant 4 is at the heart of the operation.
The midsection is built in a Northrop Grumman plant in California, and the plane’s tail is built in the United Kingdom, which is the United States’ closest F-35 partner. These pieces come together for final assembly in Fort Worth, where the front section is manufactured. There are also final F-35 assembly facilities in Italy and Japan.
Many people in the city know someone who works on the F-35, or at the very least, within the plant. Local pride in the aircraft abounds, so much so that it is beginning to compete with the steer and the oil derrick as a civic symbol. Every Christmas season, the city hosts a Lockheed Martin-sponsored college football bowl game. F-35s fly above the Amon G. Carter Stadium on game day. In the lead-up to the 2016 bowl game, locals waited in long lines in downtown Fort Worth for a chance to climb into the cockpit of an F-35 model.
The facility is the third-largest employer in Fort Worth and claims to directly or indirectly employs about 55,500 Texans, according to Lockheed Martin.
The jet was proposed in 1990s, after a rocky time for Fort Worth.
The local congressman, Jim Wright, had recently fallen from power as the U.S. speaker of the House, diminishing the area’s political clout. And then came the drawdown of the Cold War defense spending after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Fort Worth, with its air base and local defense contractors, was hit particularly hard.
In 1991, then-U.S. Defense Secretary Dick Cheney recommended the closure of Carswell Air Force Base and months later, canceled another Fort Worth plane project, the A-12, at the next-door plant.
But a few years later, the base was repurposed and military planners announced the need for a new generation of fighter planes. American leaders decided to replace various models of planes with a single plane that functioned almost like a Swiss Army knife.
The result was the F-35, a plane that can dogfight, drop bombs, shoot missiles, conduct reconnaissance, fly stealth and supersonic and offers its single pilot a situational awareness that was inconceivable a generation ago. There are three different versions of the plane, to accommodate the different types of landings and take offs: land-based runways, aircraft carriers and vertical hovering.
But its many competing goals meant the plane was overweight, over-budget and late, incurring the wrath of those worried about military spending. A Congressional Research Service analysis earlier this year of the plane estimated the plane’s production and maintenance will eventually cost $1 trillion.
In 2016, the F-35 ran into serious trouble after President Donald Trump won the presidential election. That December, a briefing for the president-elect included a chart noting a history of trouble, cataloging lapsed deadlines, design flaws and including the language, “Difficult to Overcome a Troubled Past, but Program is Improving.”
“The F-35 program and cost is out of control,” Trump tweeted that month. “Billions of dollars can and will be saved on military (and other) purchases after January 20th.”
The comments set off panic in Fort Worth.
Two Texas leaders most closely identified with the F-35 were junior members when military planners dreamed up the plane. As criticism mounted over the years, U.S. Reps. Mac Thornberry of Clarendon and Kay Granger, the former Fort Worth mayor, matured in power, and successfully pursued Congressional assignments that allowed them to protect the plane.
From these perches, Thornberry, who retired last year, and Granger delicately defended the F-35, amid the rancor around its spending.
Veasey, the Fort Worth congressman, has lived with the plane’s development his entire career. As a Congressional staffer in 1996, he attended the announcement that Lockheed Martin would compete for the government contract. Now in Congress himself, he oversees the F-35 also as a member of the House Armed Services Committee.
Other Texas officeholders like U.S. Sen. John Cornyn have kept up the drumbeat of support, signaling their support for the F-35, including via letters to Congressional leaders.
Feels “like the ’80s all over again”
Not every country can purchase an F-35 from Lockheed. A group of eight countries joined together early on to share the costs and take part in the production of the plane. Since then, other countries have earned approval to buy the plane through a government program called Foreign Military Sales.
In the international community, there are defense and economic alliances, like NATO and the European Union. But there is also something of an F-35 club, and American officials who support the plane’s development argue that the draw of membership is part of the power of the plane.
“Look at the countries that want to buy it, and those countries want to be a part of this generation of aircraft,” said U.S. Rep. August Pfluger of San Angelo, who is a retired Air Force fighter pilot and sits on the House Foreign Affairs Committee.
He added: “It strengthens our bonds with those countries. It strengthens our relationships by saying, ‘We trust you. We want to have closer relationships with you. We want to deter the same enemies that you want to deter.’”
It is such an advanced tool that maintenance — particularly in the realm of software development — is likely to keep countries closer to Lockheed and the United States.
“At the operational level, it allows our pilots and our war planners and our military professionals to have a platform and a common language, a common weapons system to fight with,” Pfluger said.
“Diplomatically, it’s very, very important,” he added.
Michael O’Hanlon, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution think tank, said those alliances extend beyond NATO, pointing to the Finland purchase. The F-35 “tightens our [bonds] with certain non-NATO countries (esp Finland, in fact) that may complicate any designs Putin would have to attack say the Nordic states,” he wrote in an email to the Tribune.
It’s a sentiment with which Kaikkonen agreed in a U.S. Air Force news release.
“Building on our great F-18 cooperation since the 1990’s, the F-35 program will be a solid foundation for the Finland and United States defense relationship in the coming decades,” he said.
O’Hanlon noted the F-35’s other diplomatic play: Putin deterrence.
By loading up the western side of the Russian border with F-35s, it’s a near constant reminder to Russian President Vladimir Putin of American military strength.
“It helps reinforce deterrence of Putin should he consider any moves against NATO states,” O’Hanlon wrote to the Tribune. “The geography of Europe, with lots of airfields within combat range of Russia, makes the F-35 especially relevant to that theater.”
Senate Armed Services Committee Chairman Jack Reed of Rhode Island suggested last week that policymakers will keep a close eye on how the F-35 performs in Europe.
“Once we have reached the point of validation, and particularly observing what they do in Europe, we can be more confident going forward with the system,” he said, according to Air Force Magazine.
Veasey, the Fort Worth congressman, grew up near the Fort Worth defense plant and the Naval Air Station Joint Reserve Base, which was once Carswell Air Force Base. Throughout his boyhood, planes roared overhead, taking part in test flights and exercises. The racket above is known colloquially as “the sound of freedom.”
The exercises continue to this day, but Cold War intrigue and paranoia long ago faded in Cowtown. Veasey said last week the future is back in his hometown.
“I’ve seen the ups and downs, and it is really crazy because of what’s happening in Europe right now,” he said. “It really does feel like the ’80s all over again.”


 eurasiantimes.com
eurasiantimes.com
F35 already has heat dissipation problems. With new engine and higher electrical output, it will be worst.When will the U.S. finally have an improved engine for the F-35?
How long will it take to re-engine the F-35s in service or to replace them with each of the new engines (EEP, AETP or the new one for the F-35B) ?
Note that re-engining is necessary, but not for a propulsion problem, much more for a problem of available electrical power. I'm going to correct several errors that we see regularly.
- The current problem of electrical power is not caused by a non-respect of the specifications but by an increase in power needs due to more and more greedy onboard equipment.
- This increased need for electrical power means that the power module is regularly used beyond its operating range and must therefore be changed much more often than expected. Until now, choices have been made to save this module either by flying less or by not operating all the onboard equipment at the same time, which has a significant operational impact. For some time now, therefore, rather than accepting operational constraints, logistical and financial constraints have been accepted. I mean that the number of workshops capable of changing the module (an operation that lasts about a hundred days) have been multiplied by three for the moment. The financial constraint is the investment in these heavy maintenance workshops and the purchase of these modules which represent 40% of the value of an engine about every 1000 flight hours. Now that these workshops and modules have been delivered, the operational constraint is less important, so we are seeing more and more articles talking about omni-purpose missions, and we are also seeing that the FMC criterion is being used more and more. I have also noticed that the number of flight hours per month is increasing again, but not in an extraordinary way.
Why has this happened?
- Mainly because the computer development time has been too long. The consequence is that it was necessary to integrate in the block definitions evolutions that were not foreseen at the beginning, evolutions that often require more energy such as radar, EW systems, optics, screens, computing power, etc., etc. Block 4 pushes the need for electrical power too far. A solution is imperative.
Could the JPO do otherwise?
Yes, perhaps, but in this case it was first necessary to be less ambitious on each of the versions and then it was necessary that the manufacturers systematically deliver better products than expected in order to be able to erase the possible margin overruns of the others. But being less ambitious means putting less powder in the eyes of the buyers, which is out of step with the State Department's wishes. And delivering equipment that performs better than expected is not acceptable from the point of view of a U.S. manufacturer unless the gains are billed in some way, so no investment in excessive performance gains.
Have the US learned any lessons from this?
Yes on the NGAD. No on the F-35.
The NGAD signals the need to return to simpler vectors that a single generation of engineers can follow from A to Z. The notion of version is secondary, if not useless.
The F-35 continues to evolve in line with the logic of the blocks, which continue to see their definition change along the way towards "even more". For the engine, the US can choose between a more generous evolution of an engine that will provide more electrical power but will be quickly caught up by the ever-increasing need for electrical power, or engines that are much more generous in terms of electrical power but whose integration will be a real challenge. the EEP can only be a very temporary engine with this logic.
What are the consequences for the current fleet?
Without new engines: more flight hours since the logistics can follow, but many more scheduled shutdowns and a much higher unit cost of ownership. No switch to block 4.
With EEP: a large part of the "block4 ready" fleet will switch to block4 without any power concerns and without any significant integration risk, but block5 will pose the same problem of power requirements.
With AETP & new f-35B engines : very high integration risks but much more power margin.


Just wait till AMCA.South Korea to buy 20 more F-35s
By Daehan Lee
Jul 20, 07:30 PM
Defense News , Jul 20, 07:30 PM
SEOUL — South Korea will buy 20 more F-35A fighter jets from the United States, as a part of its F-X project focused on acquiring foreign stealth fighter jets from 2023 to 2028.
The nation’s Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s promotion committee, led by Defense Minister Jong-sup Lee, on July 15 formally decided to buy 20 additional F-35As for 3.9 trillion Korean won (nearly $3 billion). South Korea plans to acquire them by 2028.
KF-21 is good but F-35 is still needed to fill the high-end gap.
I really hope AMCA is not delayedJust wait till AMCA.
