India's Moon Exploration Program
- Thread starter Indx TechStyle
- Start date
More options
Who Replied?- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Chandryaan-3 July launch likely. Mission cost now: INR 615 Crores
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
ISRO has begun the final assembly of the scientific payloads onto the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft!
After this, there'll be some pre-shipment tests and then the CY-3 stack will be shipped to Sriharikota. ISRO is confident about meeting the mid-July launch window. #ISRO #Chandrayaan3
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Twitter thread from Chetham Kumar on Cdy-3
In a key milestone, #Chandrayaan3 project team, which is burning the midnight oil to meet the mid-July window for the launch, has begun the process of final assembly of payloads at the UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) in Bengaluru. 1/n
@isro has adopted a cautious approach for the mission with chairman S Somanath having categorically directed scientists and engineers working on the project to ensure validation of all technologies, systems and subsystems. 2/n
“The mission progress is on the intended path with most major tests having been completed. Project team is confident of achieving the remaining progress... 3/n
... — integration of payloads and pre-shipment assessments — before Chandrayaan-3 leaves for SHAR (spaceport),” Sudheer Kumar, director, Isro Capacity Building Programme Office (CBPO), said. 4/n
In March first week, #Chandrayaan3 completed essential tests that validated its capability to withstand the harsh vibration and acoustic environment that it would face during launch. These tests are an essential part of qualification & acceptance for any spacecraft. 5/n
Unlike its predecessor, Chandrayaan-2 which carried an orbiter along with a lander and rover, Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft is a composite of three modules: Propulsion, lander and rover. 6/n
While lander & rover will carry 4 & 2 payloads, respectively, propulsion module, whose job as per initial plan was to only carry lander & rover to the lunar orbit (until separation), will also have a payload called Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE). 7/n
@isro, while describing the objective of this payload, says: “Future discoveries of smaller planets in reflected light would allow us to probe into a variety of exoplanets [a planet outside the solar system] which would qualify for habitability, or for presence of life.” 8/n
The space agency, which had failed to soft-land Vikram, the Chandrayaan-2 lander on Moon in September 2019, has worked on multiple technologies on the Chandrayaan-3 lander as reported earlier by me. 9/n
And Isro is confident of meeting the mission objectives: Demonstrate safe and soft landing; demonstrate rover roving on Moon and to conduct in-situ scientific experiments. 10/n
…The agency has improved some technologies that existed on the previous lander while also including newer ones for enhancing efficiency and redundancies. 11/n
To demonstrate advanced technologies in earth condition, several lander special tests have been carried out successfully. According to Isro, these tests are: Integrated cold test for demonstration of integrated sensors & navigation performance test… 12/n
…integrated hot test for demonstration of closed loop performance test with sensors, actuators and navigation-guidance-and-control; and lander leg mechanism performance test on a lunar simulant test bed simulating different touch down conditions. 13/n
As per an earlier update from the agency, the primary landing site for Chandrayaan-3 is between Manzius U and Boguslawski M craters. n/n
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
ISRO getting ready for Chandrayaan-3 mission in July 2nd week Senior official
Bengaluru, May 18 (PTI) If things go as planned, the Indian Space Research Organisation would launch its ambitious Chandrayaan-3 mission aimed at demonstrating critical technologies to land the spacecraft on the south pole of the moon in less than two months.
Chandrayaan-3 mission carries scientific instruments to study the thermo-physical properties of the lunar regolith, lunar seismicity, lunar surface plasma environment and elemental composition in the vicinity of the landing site.
"Chandrayaan-3 mission is scheduled in July second week," a senior official of the Bengaluru-headquartered national space agency under the Department of Space told PTI on Thursday.
While the scope of these scientific instruments on the lander and the rover would fit in the theme of 'Science of the Moon', another experimental instrument would study the spectro-polarimetric signatures of the Earth from the lunar orbit, which would fit in the theme of 'Science from the Moon', according to ISRO officials.
In March this year, Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft successfully completed the essential tests that validated its capability to withstand the harsh vibration and acoustic environment that the spacecraft would face during its launch.
These tests were particularly challenging, considering the fact that the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, which would be launched by LVM3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-III) (earlier referred as GSLV Mk III) from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota, is a composite of three modules -- propulsion, lander and rover.
"Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It consists of Lander and Rover configuration", an ISRO official said.
The propulsion module, which has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit, would carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit.
Lander payloads are: 'Chandra's Surface Thermophysical Experiment' to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature; 'Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity' for measuring the seismicity around the landing site; and 'Langmuir Probe' to estimate the plasma density and its variations.
A passive Laser Retroreflector Array from the US space agency, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is also accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover payloads are: 'Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer' and 'Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy' for deriving the elemental composition in the vicinity of the landing site.
The Lander would have the capability to soft land at a specified lunar site and deploy the Rover which would carry out in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface during the course of its mobility.
(This story has not been edited by THE WEEK and is auto-generated from PTI)The main function of the propulsion module is to carry the lander module from launch vehicle injection till final lunar 100 km circular polar orbit and separate it. Apart from this, the propulsion module also has one scientific payload as a value addition which would be operated post separation of the lander module, it was noted.
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Exclusive: Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft arrives at India's spaceport in preparation for July launch

“Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft is a composite of three modules: Propulsion Module, Lander Module and the Rover module," ISRO had said in March 2023. Photograph: (WION)
WION Exclusive: Chandrayaan-3 will be the sixth orbital flight of the LVM3 rocket, which has so far delivered successes in all its missions

“Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft is a composite of three modules: Propulsion Module, Lander Module and the Rover module," ISRO had said in March 2023. Photograph: (WION)
WION Exclusive: Chandrayaan-3 will be the sixth orbital flight of the LVM3 rocket, which has so far delivered successes in all its missions
The spacecraft that the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) hopes to land on the moon later this year, has been wheeled into the country's spaceport, Satish Dhawan Space Centre, WION has learnt.
Named as Chandrayaan-3 (Sanskrit for Moon Vehicle-3), this will be India's third lunar mission and will attempt both controlled soft-landing on the lunar surface and in-situ analysis by the means of a rover.
In the evening hours on Friday, the slow-moving, specialised truck ferrying the spacecraft from UR Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru arrived at India's spaceport, under a security blanket.
The UR Rao Satellite Centre is where India's satellites and interplanetary probes are designed, developed and tested.
They are then trucked to the spaceport, where final integration and testing, filling of fuels are carried out, prior to launch.
Owing to the sensitive electronics and space-grade components on-board, the satellite is always placed in a clean room and transported in such conditions. A clean room is a specialised facility where the pressure, temperature and humidity are kept constant regardless of the weather outside. Clean rooms also have negligible amounts of dust particles per cubic metre of air.
Meanwhile, fast-paced activity is underway at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre to assemble and ready India's heaviest rocket LVM3 (earlier known as Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark 3), which is meant to loft the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft into an orbit around the earth, from where it will begin its weeks-long journey to the moon.
Chandrayaan-3 will be the sixth orbital flight of this rocket, which has so far delivered successes in all its missions (including two commercial missions).
In March this year, ISRO had announced that the Chandrayaan-3 integrated spacecraft, comprising the propulsion module, lander and rover, underwent tests to check whether it can handle the excess amounts of noise and vibration that are generated at the time of the rocket's launch and flight.
For context, the sound emanating from the launch of the LVM3 rocket(which is meant to launch Chandrayaan-3) can be heard at least within an eight-kilometer radius around the launchpad.
Nestled securely in the nosecone (payload fairing) of the rocket, the spacecraft would have to operate normally even after being exposed to such noise and vibration at launch.
Though the payload fairing is adequately protected to shield the spacecraft from the harsh launch environment, it is essential to test and ensure the survivability of the spacecraft.
These tests were particularly challenging, considering the fact that the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft is a composite of three modules: Propulsion Module, Lander Module and the Rover module," ISRO had said in March. The vibration and acoustic tests carried out on the integrated spacecraft have provided sufficient confidence in the structural integrity and survivability in the launch environment, the Indian Space agency had added.
Earlier this year, speaking at the Indian Science Congress, Dr. S. Somanath, Chairman ISRO and Secretary, Department of Space, had said that the mission goals of Chandrayaan-3 are the same as that of its predecessor Chandrayaan-2 which was launched in 2019. He had said that the primary objective is to carry out a safe Lunar landing and ensure that the on-board rover can exit the lander and traverse on the Lunar surface.
In 2019, the Chandrayaan-2 mission could not make a controlled Lunar landing (it had crash landed). Following this, ISRO took multiple measures to ensure that the third Lunar mission could accomplish what its predecessor couldn't. These measures include software changes, changes in the propulsion system, new sensors, ruggedisation to handle unexpected situations and failures.
Notably, the Chandrayaan-3 mission will only be carrying a Lunar lander, rover and propulsion module, unlike its predecessor which carried an orbiter, lander and rover. According to ISRO, the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter is functional and continues to perform its imaging and remote sensing role from an altitude of 100kms above Lunar surface.
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Cdy-3 page on ISRO website updated.
Chandryaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It consists of Lander and Rover configuration. It will be launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit. The propulsion module has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.
Lander payloads: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature; Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) for measuring the seismicity around the landing site; Langmuir Probe (LP) to estimate the plasma density and its variations. A passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA is accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover payloads: Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) for deriving the elemental composition in the vicinity of landing site.
Chandrayaan-3 consists of an indigenous Lander module (LM), Propulsion module (PM) and a Rover with an objective of developing and demonstrating new technologies required for Inter planetary missions. The Lander will have the capability to soft land at a specified lunar site and deploy the Rover which will carry out in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface during the course of its mobility. The Lander and the Rover have scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface. The main function of PM is to carry the LM from launch vehicle injection till final lunar 100 km circular polar orbit and separate the LM from PM. Apart from this, the Propulsion Module also has one scientific payload as a value addition which will be operated post separation of Lander Module. The launcher identified for Chandrayaan-3 is GSLV-Mk3 which will place the integrated module in an Elliptic Parking Orbit (EPO) of size ~170 x 36500 km.
The mission objectives of Chandrayaan-3 are:
The objectives of scientific payloads planned on Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module and Rover are provided below:
Three dimensional views of Chandrayaan-3 modules are provided below:
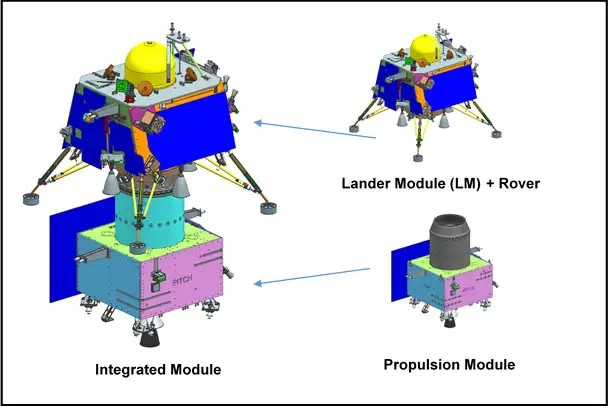
Chandrayaan-3 – Elements
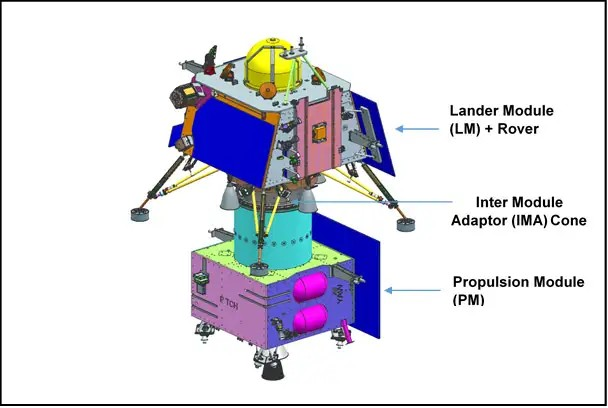
Chandrayaan-3 – Integrated Module
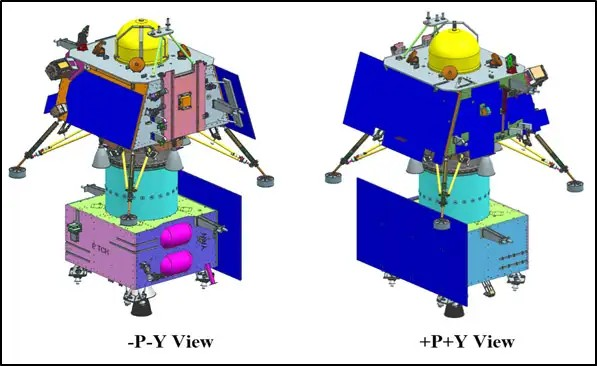
Chandrayaan-3 Integrated Module - Views
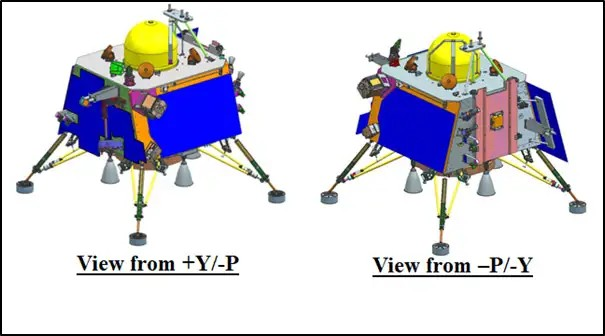
Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module -Views
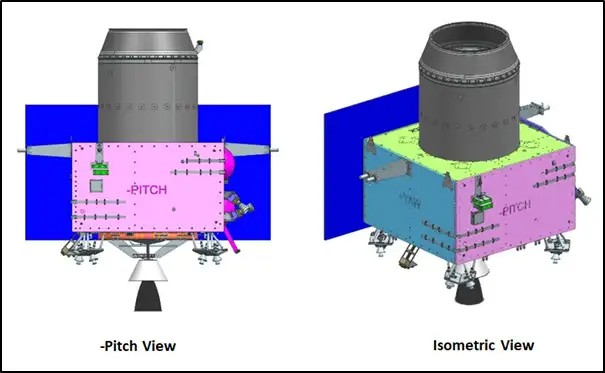
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module - Views

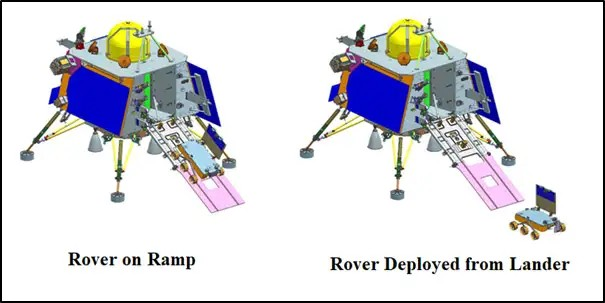
Chandrayaan-3 Rover on Ramp and Deployed Views
Chandrayaan-3 Rover -Views
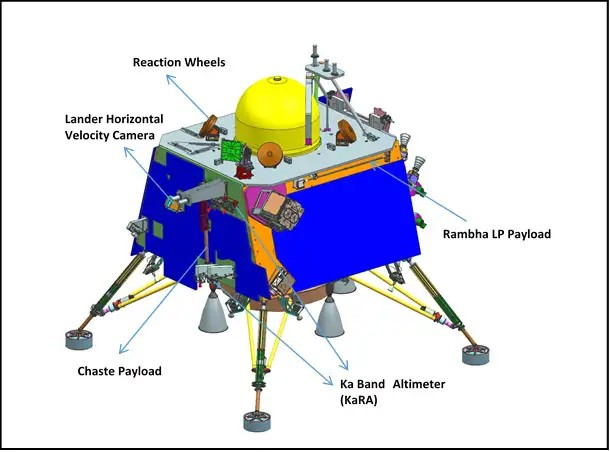
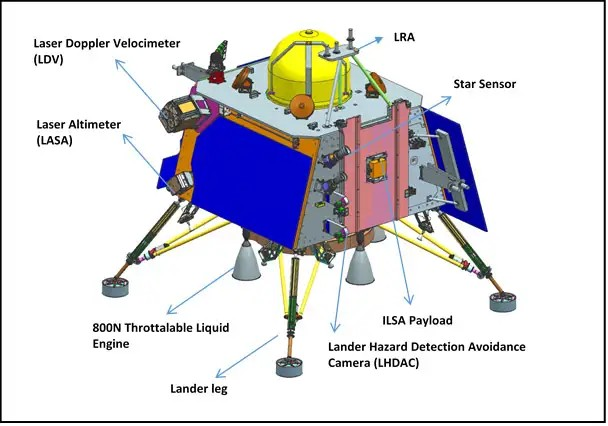
Chandrayaan-3 Lander
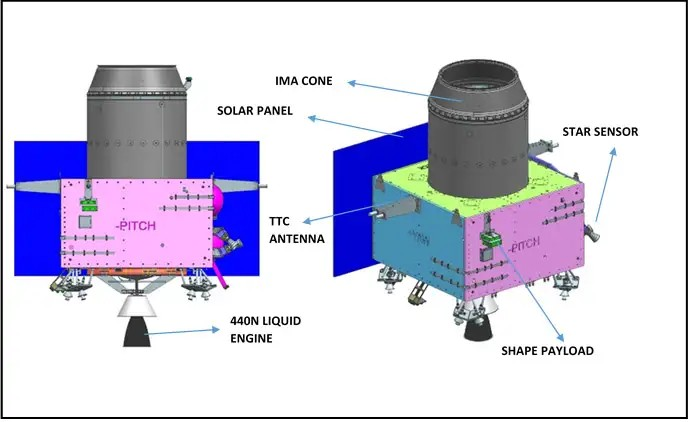
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module
Chandryaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It consists of Lander and Rover configuration. It will be launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover configuration till 100 km lunar orbit. The propulsion module has Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload to study the spectral and Polari metric measurements of Earth from the lunar orbit.
Lander payloads: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE) to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature; Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) for measuring the seismicity around the landing site; Langmuir Probe (LP) to estimate the plasma density and its variations. A passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA is accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover payloads: Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) for deriving the elemental composition in the vicinity of landing site.
Chandrayaan-3 consists of an indigenous Lander module (LM), Propulsion module (PM) and a Rover with an objective of developing and demonstrating new technologies required for Inter planetary missions. The Lander will have the capability to soft land at a specified lunar site and deploy the Rover which will carry out in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface during the course of its mobility. The Lander and the Rover have scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface. The main function of PM is to carry the LM from launch vehicle injection till final lunar 100 km circular polar orbit and separate the LM from PM. Apart from this, the Propulsion Module also has one scientific payload as a value addition which will be operated post separation of Lander Module. The launcher identified for Chandrayaan-3 is GSLV-Mk3 which will place the integrated module in an Elliptic Parking Orbit (EPO) of size ~170 x 36500 km.
The mission objectives of Chandrayaan-3 are:
- To demonstrate Safe and Soft Landing on Lunar Surface
- To demonstrate Rover roving on the moon and
- To conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
- Altimeters: Laser & RF based Altimeters
- Velocimeters: Laser Doppler Velocimeter & Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera
- Inertial Measurement: Laser Gyro based Inertial referencing and Accelerometer package
- Propulsion System: 800N Throttleable Liquid Engines, 58N attitude thrusters & Throttleable Engine Control Electronics
- Navigation, Guidance & Control (NGC): Powered Descent Trajectory design and associate software elements
- Hazard Detection and Avoidance: Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Processing Algorithm
- Landing Leg Mechanism.
- Integrated Cold Test - For the demonstration of Integrated Sensors & Navigation performance test using helicopter as test platform
- Integrated Hot test – For the demonstration of closed loop performance test with sensors, actuators and NGC using Tower crane as test platform
- Lander Leg mechanism performance test on a lunar simulant test bed simulating different touch down conditions.
| Sl No. | Parameter | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mission Life (Lander & Rover) | One lunar day (~14 Earth days) |
| 2. | Landing Site (Prime) | 4 km x 2.4 km 69.367621 S, 32.348126 E |
| 3. | Science Payloads | Lander:
|
| 4. | Two Module Configuration |
|
| 5. | Mass |
|
| 6. | Power generation |
|
| 7. | Communication |
|
| 8. | Lander Sensors |
|
| 9. | Lander Actuators | Reaction wheels – 4 nos (10 Nms & 0.1 Nm) |
| 10. | Lander Propulsion System | Bi-Propellant Propulsion System (MMH + MON3), 4 nos. of 800 N Throttleable engines & 8 nos. of 58 N; Throttleable Engine Control Electronics |
| 11. | Lander Mechanisms |
|
| 12. | Lander Touchdown specifications |
|
The objectives of scientific payloads planned on Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module and Rover are provided below:
| Sl. No | Lander Payloads | Objectives | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA) | Langmuir probe (LP) | To measure the near surface plasma (ions and electrons) density and its changes with time |
| 2. | Chandra’s Surface Thermo physical Experiment (ChaSTE) | To carry out the measurements of thermal properties of lunar surface near polar region. | |
| 3. | Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA) | To measure seismicity around the landing site and delineating the structure of the lunar crust and mantle. | |
| 4. | LASER Retroreflector Array (LRA) | It is a passive experiment to understand the dynamics of Moon system. |
| Sl. No | Rover Payloads | Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS) | Qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis & To derive the chemical Composition and infer mineralogical composition to further our understanding of Lunar-surface. |
| 2. | Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) | To determine the elemental composition (Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca,Ti, Fe) of Lunar soil and rocks around the lunar landing site. |
| Sl. No | Propulsion Module Payload | Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) | Future discoveries of smaller planets in reflected light would allow us to probe into variety of Exo-planets which would qualify for habitability (or for presence of life). |
Three dimensional views of Chandrayaan-3 modules are provided below:
Chandrayaan-3 – Elements
Chandrayaan-3 – Integrated Module
Chandrayaan-3 Integrated Module - Views
Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module -Views
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module - Views
Chandrayaan-3 Rover on Ramp and Deployed Views
Chandrayaan-3 Rover -Views
Chandrayaan-3 Lander
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Continued..
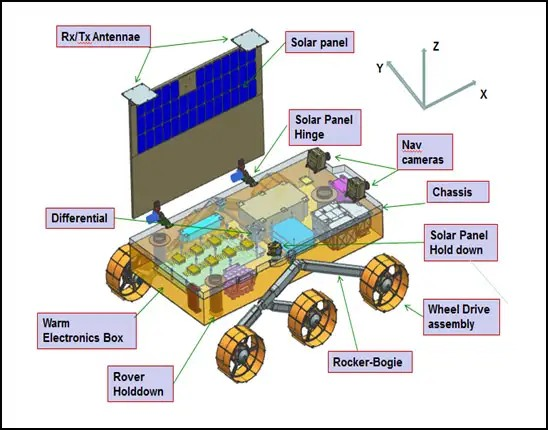
Chandrayaan-3 Rover
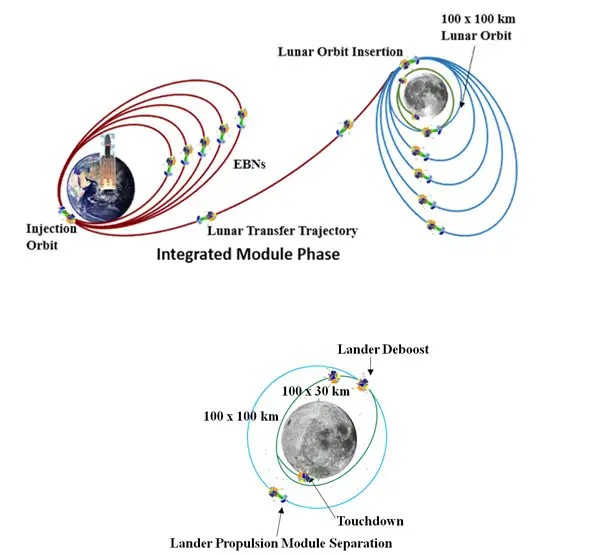
Chandrayaan-3 – Mission Profile
Chandrayaan-3 Rover
Chandrayaan-3 – Mission Profile
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Just 3 weeks to go for launch.
Any activities noted around launch pad yet?
Any activities noted around launch pad yet?
Vamsi
New Member
- Joined
- Jun 27, 2020
- Messages
- 4,858
- Likes
- 29,461
nope, no NOTAM yetJust 3 weeks to go for launch.
Any activities noted around launch pad yet?
Vamsi
New Member
- Joined
- Jun 27, 2020
- Messages
- 4,858
- Likes
- 29,461
NOTAM is outJust 3 weeks to go for launch.
Any activities noted around launch pad yet?
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
This source though says launch date to be between 12 to 19 July.NOTAM is out

Chandrayaan 3: ISRO’s Third Moon Mission
The Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, is all set to embark on its upcoming lunar mission, Chandrayaan 3.
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
NOTAM is out
What is the time frame considered for post-launch debris decay?This source though says launch date to be between 12 to 19 July.

Chandrayaan 3: ISRO’s Third Moon Mission
The Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, is all set to embark on its upcoming lunar mission, Chandrayaan 3.telanganatoday.com
If 1 week, then around 19 July, if 2 weeks, then 12 July.
Vamsi
New Member
- Joined
- Jun 27, 2020
- Messages
- 4,858
- Likes
- 29,461
I don't knowWhat is the time frame considered for post-launch debris decay?
If 1 week, then around 19 July, if 2 weeks, then 12 July.
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,416
- Likes
- 56,946
Activities for Chandryaan-3 launch campaign have begun in SHAR!
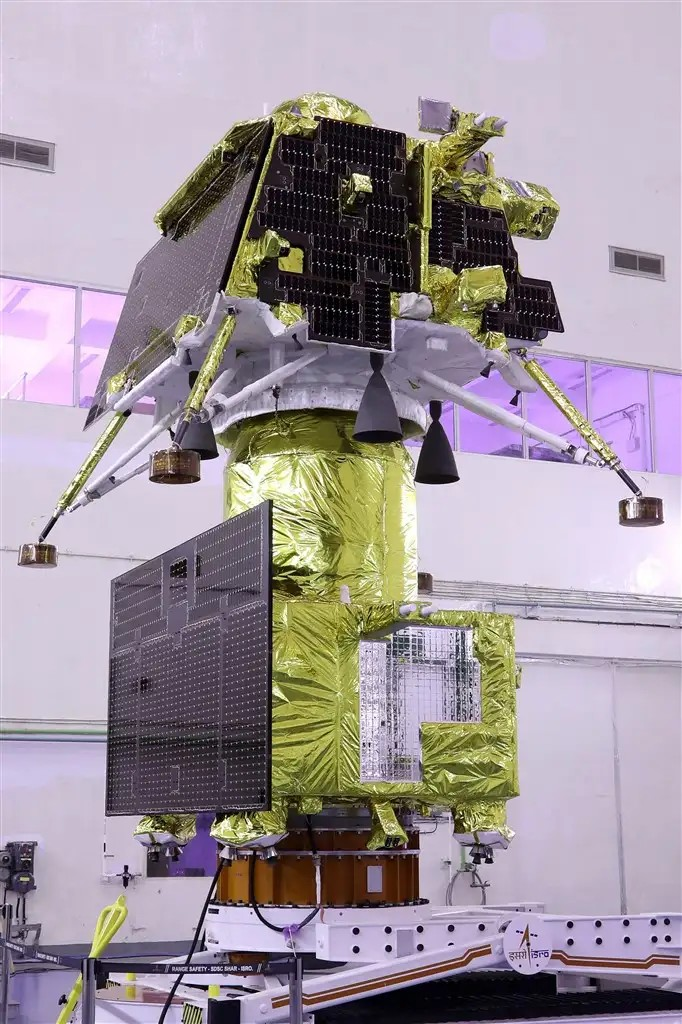
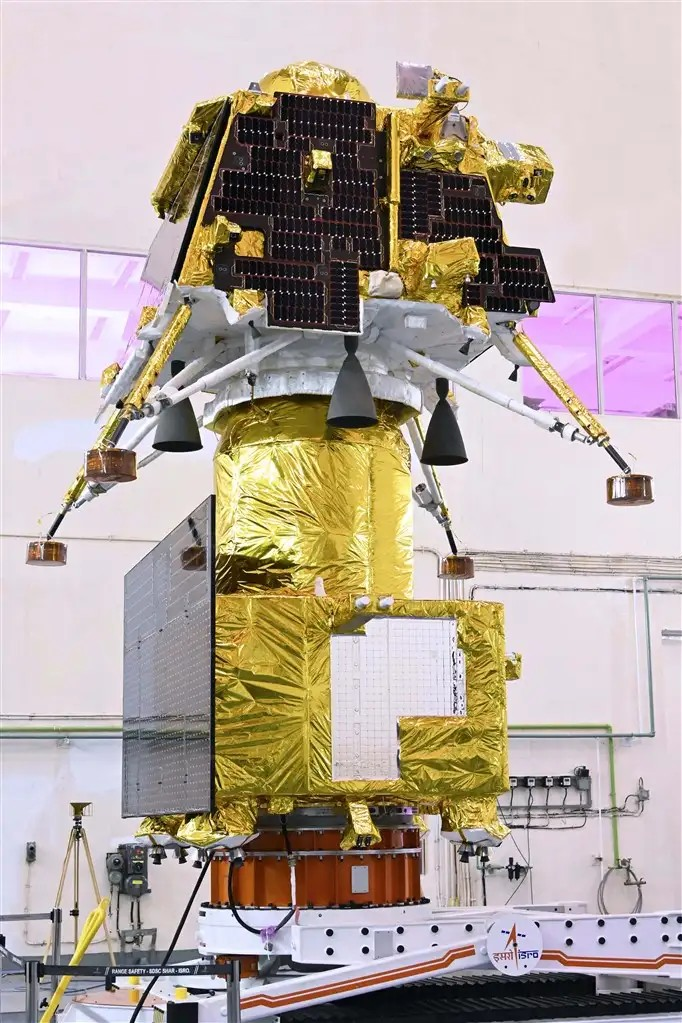
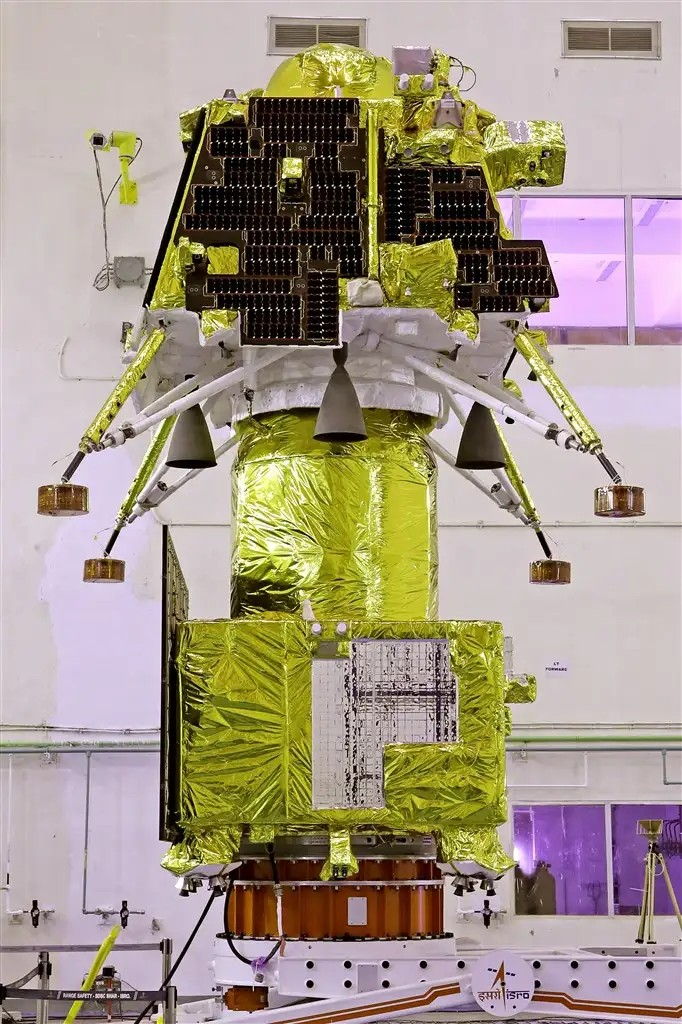
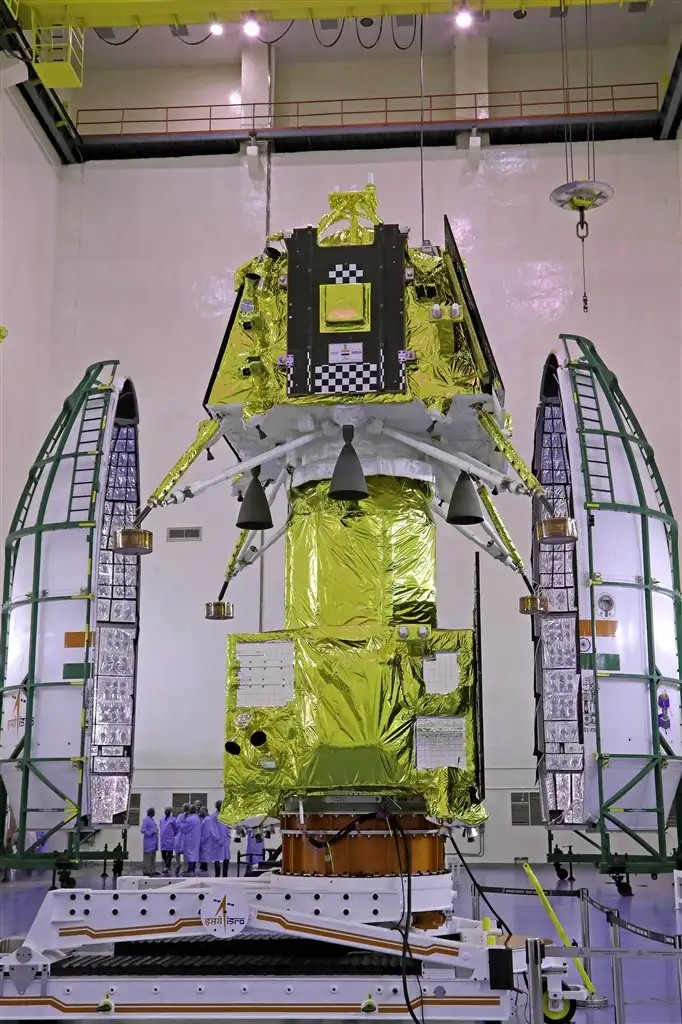




New photos from galleryThe Chandrayaan-3 stack has been encapsulated in GSLV Mk-3's payload fairing!! The next step is going to be stacking the rocket and then integrating the fairing assembly with it. #ISRO #Chandrayaan3
Last edited:
Articles
-
India Strikes Back: Operation Snow Leopard - Part 1
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 9
-
Aftermath Galwan : Who holds the fort ?
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 33
-
The Terrible Cost of Presidential Racism(Nixon & Kissinger towards India).
- ezsasa
- Replies: 40
-
Modern BVR Air Combat - Part 2
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 22
-
Civil & Military Bureaucracy and related discussions
- daya
- Replies: 32
