jakojako777
New Member
- Joined
- Oct 27, 2009
- Messages
- 2,957
- Likes
- 40
Radar 96l6e
RADAR 96L6E
Summary
96L6ERadiolokatsionnaya radar station - all-altitude detector (TSBs) 96L6E designed for the detection and measurement of target coordinates (azimuth, elevation, distance), can be included in the composition of S-300PMU, S-300PMU1 and S-300PMU2 as a stand-alone tool targeting SAMs 90ZH6E, 90ZH6E1, 90ZH6E2 and mates with MP ACS type "Baikal-1E", "Senezh-M1E" or manual RTV-type base-1E "," Field-E.
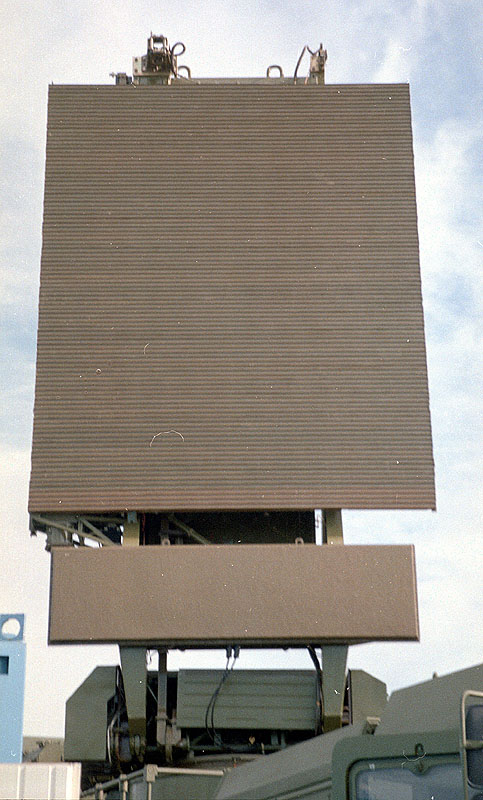
Radar 96L6E with a full-azimuth multi-beam antenna array, providing scanning beam in uglomestnoy plane, automatically delivers the ROP 30N6E, 30N6E1, 30N6E2 information about the air conditions on a wide range of aerodynamic targets: aircraft, cruise missiles (including the construction of stealth technology ) and the means of the WTO. Due to the use of adaptive shirokobazovyh signals and multifrequency radar work provides a highly efficient detection of both low-altitude targets and goals for the medium and high altitudes. To detect targets at extremely low altitudes in the forest and rough terrain antenna device locator can be raised on a special tower - 966AA14.
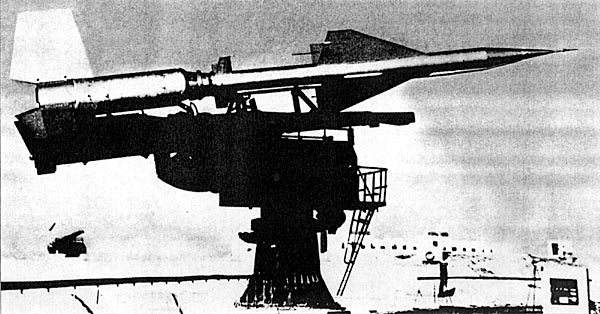
Layout radar 96L6E exhibition MAKS-97 © Nevsky Bastion
Radar 96L6E provides: a review of specified areas of detection and automatic selection of priorities for the drawstrings routes; auto-runs on auto tracking purposes (bearings) by assigning numbers, identification of nationality purposes; automatic selection of priorities for the issuance of ZU for ROP; automatic issue of ROP target coordinates accompanied by the ROP, to ensure coordinate support, recognition of 4 classes of goals - airplanes, helicopters, UAVs and missiles.
Pair radar 96L6E with S-300PMU, S-300PMU1 carried by cable, with S-300PMU2 pairing is carried out using remote workplace 965RR03E on microwave and fiber-optic communication lines.
Radar 96L6E
Radar 96L6E in stowed position to a transport unit - MZKT-7930 "astrologer" © FGUP LEMZ "
Radar 96L6E
Radar 96L6E in firing position on the two transport units in the shop FGUP LEMZ "© FGUP LEMZ"
Radar 96L6E has two versions: one version of the execution of the transport unit; variant execution on two transport units.
In the embodiment of performance on a transport unit of the radar 96L6E includes: antenna device 966AA01E; container 966FF03E with receiving and transmitting equipment, information processing equipment, operator's station, communications equipment and system of national identification, a set of APP-0; TM966E transport vehicle on the basis of self-propelled chassis MZKT-7930 "astrologer", with a system of autonomous power supply BOT-2L on the basis of the generator power takeoff from the engine self-propelled chassis, a set of cables.
In the embodiment of performance of two transport units of the radar 96L6E includes: Antenna 966AA00E - combination of Trucks and semi-trailer, which contains 966AA01E antenna device, the system of autonomous power supply SPS-75 (SES-75M), or similar, set of cables, hardware post 966FF00E - combination of Trucks and semi-trailer, which contains the container 966FF03E with autonomous power supply system SES-75 (SES-75M), or similar.
Option execution 96L6E two transport units allows for spacing to position the antenna and hardware posts up to 100 m.
Radar 96L6E can be given: a means of external power supply 98E6U; cars for towing 98E6U; 966AA14 tower - a tower equipped with 40V6M trucks for transportation of the MAZ-537G (74106) Remote operator station (up to 4), a set of APP Group P28E.
Electricity can be carried out by autonomous, built-BOT-2L, SES-75 (SES-75M), from funds given to the external power supply type 98E6U or from an industrial power through BOOT 98E6U.
Term of service - not less than 20 years.
Full service life of up to 25 000-30 000 hours in the light overhaul. Life before the first overhaul - not less than 10 years, the service life of 12 000 hours.
There is a single ZIP-0 in each radar, provided spare parts in the trailer group P28E for three radar.
Method of moving radar 96L6E - its course, run at least 10 000 km. RLS is transported by rail, water and air.
For communication on the march radar 96L6E completed voice equipment such as 14YA6-5.
Key performance characteristics
Range of radiation frequencies
"C
The presence of automatic frequency tuning
eat
The range of distances detected purposes
5-300 km
Field of view:
A) When all-altitude detection:
- Azimuth
360 °
- On the corner of the place
from -3 ° to +20 °
- On the Doppler velocity
± 30 to ± 1200 m / s
The coefficient of suppression of reflections from the underlying surface, dB
70
Rate update:
- In the lower zone from 0 to 1,5 °
6
- In the upper zone from 1,5 to 20 °
12 s
B) When the sector review:
In the sector slowing:
- Azimuth
120 °
- On the corner of the place
from 0 to 60 °
- On the Doppler velocity
from ± 50 to ± 2800 m / s
time sector review
to 8 with
Outside the sector slowing down:
- On the corner of the place
-3 to 1,5 °
time review of the lower sector
5,5 with
Full review cycle
With 13,5
B) When low-altitude detection:
- Azimuth
360 °
- On the corner of the place
0 - 1,5 °
- On the Doppler velocity
from ± 30 to ± 1200 m / s
rate review
6
Accompaniment tracks purposes is provided in the corners of the place
60 °
The number of tracked goals
100
Time straps route and issuance ZU on aerodynamic purposes:
- At angles less than 1,5 °
12 s
- At angles greater 1,5 °
21 p.
The number of false ZU 30 minutes of work
no more than 3-5
Time commitment:
for execution options for a transport unit:
- From the march
5 min
- From the unfolded state
no more than 3 minutes
- Duty of the state
not more than 40
execution options for the two transport units:
- From the march
30 min
- From the unfolded state
no more than 3 minutes
- Duty of the state
not more than 40
Time of installation of tower
2 h
The number of combat crew
3 pers.
Developer
Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Lianozovo Electromechanical Plant"







ÐÀÄÈÎËÎÊÀÖÈÎÍÍÀß ÑÒÀÍÖÈß 96Ë6Å
RADAR 96L6E
Summary
96L6ERadiolokatsionnaya radar station - all-altitude detector (TSBs) 96L6E designed for the detection and measurement of target coordinates (azimuth, elevation, distance), can be included in the composition of S-300PMU, S-300PMU1 and S-300PMU2 as a stand-alone tool targeting SAMs 90ZH6E, 90ZH6E1, 90ZH6E2 and mates with MP ACS type "Baikal-1E", "Senezh-M1E" or manual RTV-type base-1E "," Field-E.
Radar 96L6E with a full-azimuth multi-beam antenna array, providing scanning beam in uglomestnoy plane, automatically delivers the ROP 30N6E, 30N6E1, 30N6E2 information about the air conditions on a wide range of aerodynamic targets: aircraft, cruise missiles (including the construction of stealth technology ) and the means of the WTO. Due to the use of adaptive shirokobazovyh signals and multifrequency radar work provides a highly efficient detection of both low-altitude targets and goals for the medium and high altitudes. To detect targets at extremely low altitudes in the forest and rough terrain antenna device locator can be raised on a special tower - 966AA14.
Layout radar 96L6E exhibition MAKS-97 © Nevsky Bastion
Radar 96L6E provides: a review of specified areas of detection and automatic selection of priorities for the drawstrings routes; auto-runs on auto tracking purposes (bearings) by assigning numbers, identification of nationality purposes; automatic selection of priorities for the issuance of ZU for ROP; automatic issue of ROP target coordinates accompanied by the ROP, to ensure coordinate support, recognition of 4 classes of goals - airplanes, helicopters, UAVs and missiles.
Pair radar 96L6E with S-300PMU, S-300PMU1 carried by cable, with S-300PMU2 pairing is carried out using remote workplace 965RR03E on microwave and fiber-optic communication lines.
Radar 96L6E
Radar 96L6E in stowed position to a transport unit - MZKT-7930 "astrologer" © FGUP LEMZ "
Radar 96L6E
Radar 96L6E in firing position on the two transport units in the shop FGUP LEMZ "© FGUP LEMZ"
Radar 96L6E has two versions: one version of the execution of the transport unit; variant execution on two transport units.
In the embodiment of performance on a transport unit of the radar 96L6E includes: antenna device 966AA01E; container 966FF03E with receiving and transmitting equipment, information processing equipment, operator's station, communications equipment and system of national identification, a set of APP-0; TM966E transport vehicle on the basis of self-propelled chassis MZKT-7930 "astrologer", with a system of autonomous power supply BOT-2L on the basis of the generator power takeoff from the engine self-propelled chassis, a set of cables.
In the embodiment of performance of two transport units of the radar 96L6E includes: Antenna 966AA00E - combination of Trucks and semi-trailer, which contains 966AA01E antenna device, the system of autonomous power supply SPS-75 (SES-75M), or similar, set of cables, hardware post 966FF00E - combination of Trucks and semi-trailer, which contains the container 966FF03E with autonomous power supply system SES-75 (SES-75M), or similar.
Option execution 96L6E two transport units allows for spacing to position the antenna and hardware posts up to 100 m.
Radar 96L6E can be given: a means of external power supply 98E6U; cars for towing 98E6U; 966AA14 tower - a tower equipped with 40V6M trucks for transportation of the MAZ-537G (74106) Remote operator station (up to 4), a set of APP Group P28E.
Electricity can be carried out by autonomous, built-BOT-2L, SES-75 (SES-75M), from funds given to the external power supply type 98E6U or from an industrial power through BOOT 98E6U.
Term of service - not less than 20 years.
Full service life of up to 25 000-30 000 hours in the light overhaul. Life before the first overhaul - not less than 10 years, the service life of 12 000 hours.
There is a single ZIP-0 in each radar, provided spare parts in the trailer group P28E for three radar.
Method of moving radar 96L6E - its course, run at least 10 000 km. RLS is transported by rail, water and air.
For communication on the march radar 96L6E completed voice equipment such as 14YA6-5.
Key performance characteristics
Range of radiation frequencies
"C
The presence of automatic frequency tuning
eat
The range of distances detected purposes
5-300 km
Field of view:
A) When all-altitude detection:
- Azimuth
360 °
- On the corner of the place
from -3 ° to +20 °
- On the Doppler velocity
± 30 to ± 1200 m / s
The coefficient of suppression of reflections from the underlying surface, dB
70
Rate update:
- In the lower zone from 0 to 1,5 °
6
- In the upper zone from 1,5 to 20 °
12 s
B) When the sector review:
In the sector slowing:
- Azimuth
120 °
- On the corner of the place
from 0 to 60 °
- On the Doppler velocity
from ± 50 to ± 2800 m / s
time sector review
to 8 with
Outside the sector slowing down:
- On the corner of the place
-3 to 1,5 °
time review of the lower sector
5,5 with
Full review cycle
With 13,5
B) When low-altitude detection:
- Azimuth
360 °
- On the corner of the place
0 - 1,5 °
- On the Doppler velocity
from ± 30 to ± 1200 m / s
rate review
6
Accompaniment tracks purposes is provided in the corners of the place
60 °
The number of tracked goals
100
Time straps route and issuance ZU on aerodynamic purposes:
- At angles less than 1,5 °
12 s
- At angles greater 1,5 °
21 p.
The number of false ZU 30 minutes of work
no more than 3-5
Time commitment:
for execution options for a transport unit:
- From the march
5 min
- From the unfolded state
no more than 3 minutes
- Duty of the state
not more than 40
execution options for the two transport units:
- From the march
30 min
- From the unfolded state
no more than 3 minutes
- Duty of the state
not more than 40
Time of installation of tower
2 h
The number of combat crew
3 pers.
Developer
Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Lianozovo Electromechanical Plant"







ÐÀÄÈÎËÎÊÀÖÈÎÍÍÀß ÑÒÀÍÖÈß 96Ë6Å