Okabe Rintarou
New Member
- Joined
- Apr 23, 2018
- Messages
- 2,338
- Likes
- 11,996
Aim of thread
This thread aims to collect open source information on the Organisation and Equipment of an Indian Infantry Battalion. This will enable awareness about the capabilities of the Indian Infantry Battalion which forms the largest part of Indian Army. The thread further aims to make sense of the degree to which modernization has occurred in the Indian Infantry Battalions given the recent modernization of Infantry that has gathered pace under General Bipin Rawat. For example, to make sense of the requirement of rifles in Infantry to the amount of rifles ordered (72,000 ordered + 36,000 optional), it is necessary to know how many Infantry soldiers would carry them in an Infantry BattalionThe aim of opening this thread in knowledge repository section is to ensure that this particular discussion does not get buried in the news, updates, discussions and endless fantasies for Infantry Equipment Modernization. This thread is not only about Infantry Gear Modernization, the discussion thread for which, already exists. This is for making sense of what that modernization means on the ground: who gets issued what and how the tactics and capability change based on that.
Information from Internet Sources
Indian Army has 350 Light Infantry Battalions. This thread will further refer to them as "battalions". Other than them, there are 15 Parachute and SF Battalions in the Parachute Regiment and 50 Mechanised Infantry Battalions Mechanised Infantry Regiment and Brigade of the Guards. Their and Rashtriya Rifles' TO&E will not be considered here.
Sources from 2006 on the Bharat Rakshak detail, what I believe to be, the old structure, roster and equipment of battalions.
Structure:
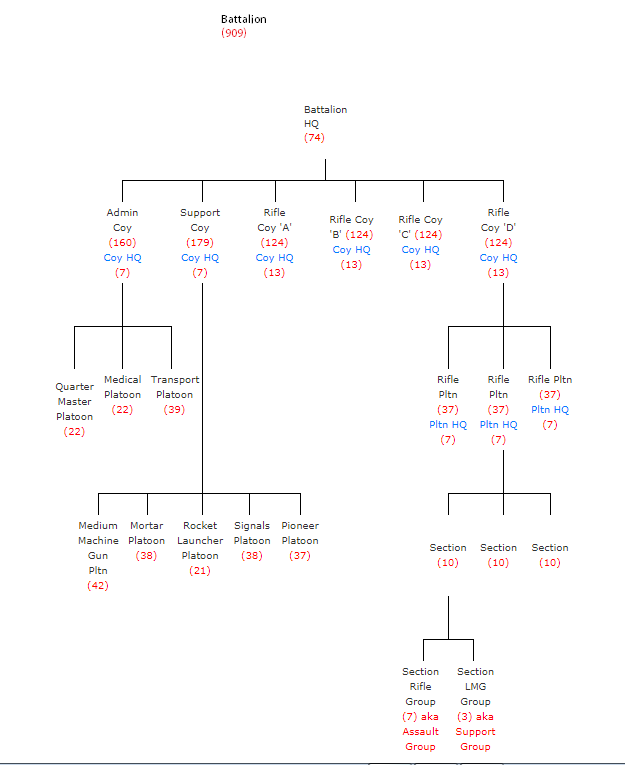
Roster:-
AUTHORISED PERSONNEL:
Equipment:-
AUTHORISED EQUIPMENT - BATTALION LEVEL:
Source: http://www.bharat-rakshak.com/ARMY/units/4-infantry-bn-structure.html
Structure:
Roster:-
AUTHORISED PERSONNEL:
| Officers | 19 |
| JCOs (Junior Commissioned Officers) | 24 |
| Other Ranks (ORs) | 787 |
| NC(E)s | 40 |
| Officer (Army Medical Corps) | 1 |
| OR (Army Medical Corps) | 22 |
| OR (Army Educational Corps) | 6 |
| OR (Electrical & Mechanical Engineers) | 8 |
| OR Others | 2 |
| Total | 909 |
Equipment:-
AUTHORISED EQUIPMENT - BATTALION LEVEL:
| Rifles | 697 |
| Light Machine Guns | 40 |
| 9mm Sub-Machine Guns | 128 |
| Pistols | 61 |
| 81mm Mortar | ? |
| 30mm AGS-17 | ? |
| 84mm Carl Gustav | ? |
| 2" Mortar | 10 |
| 3" Mortar | 8 |
| Sig Pistol | 20 |
| 75mm RCL | 4 |
Source: http://www.bharat-rakshak.com/ARMY/units/4-infantry-bn-structure.html
Updated chart in Bharat Rakshak (uploaded in 2016, data from a 1980s document)
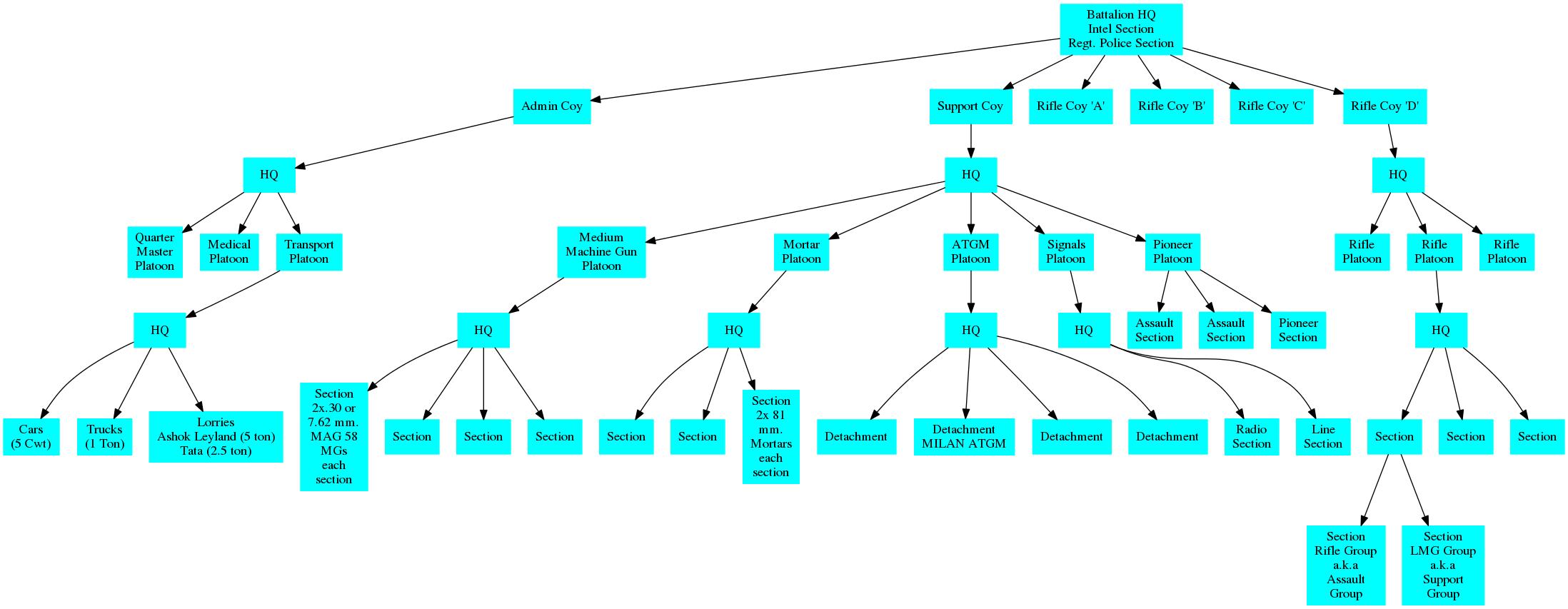
Source: http://www.bharat-rakshak.com/ARMY/...isation-of-a-standard-infantry-battalion.html

Source: http://www.bharat-rakshak.com/ARMY/...isation-of-a-standard-infantry-battalion.html
Now this 2016 source ( https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/eac...n-battle-why-the-army-cannot-downsize-1284838 ) from NDTV notes following changes in the structure and equipment:-
- 10 man section now has:-
- 2 LMG
- "1 Rocket Launcher" (RCL?)
- 700 LMG rounds on each LMG gunner.
- 500 rounds distributed and carried separately by soldiers of the section.
- In all, soldiers in a section carry 1400 rounds of LMG ammunition packed in 34 magazines on them. (confusing, should be (700X2)+500=1900)
- Four "rockets" carried with the "launcher", the section carries another six rounds on them.
- Bayonet strength a.k.a Assault Group is 6 man strong.
- LMG a.k.a. Support Group is 4 man strong now (earlier was 3).
- "
Regiment" (Battalion) Level, comprising:-- Four combat companies
- One Support and Logistic Company
- Headquarter Company
- Each
regiment(Battalion) carries with it :-- Battle field surveillance radars (BFSR-SR? first time I heard about Infantry having them)
- Snipers with at least 200 rounds of ammunition ( how many? )
- Three Multi-Barrel Grenade Launchers (MBGL)
- Three Automatic Grenade Launchers (AGL)
- Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGMs)
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) (They mean mini UAV like Netra? and ones on order like Scan Eagle? Again, hard to believe that all battalions have them)
- Heavy communication equipment
- "Over the years, vehicle drivers for instance have been trained as electricians, or to fire ATGM, man radars, double up as nursing assistant for injuries since number of battlefield nursing attendants have been cut down. Some are trained as mechanics to repair vehicles on the spot "
My (incomplete) estimate of the current Indian Infantry Battalion structure is as follows:-
- Infantry Battalion
- HQ Company (Coy)
- Battalion HQ
- C.O. (Commanding Officer)[Colonel]
- 2-I-C (Second-in-Command)[Lt. Colonel]
- Provost Section?
- Int Section?
- ?
- Medical Platoon
- ?
- Quatermaster Platoon
- ?
- Transport Platoon
- ?
- Battalion HQ
- Support and Logistics Coy
- Company HQ
- O.C. (Officer Commanding)[Major]
- Second in Command[Captain]
- ?
- MMG Platoon
- 4XMMG Sections
- 2X MAG 58 MMG
- 4XMMG Sections
- Mortar Platoon
- 3X Mortar Sections
- 2X 81mm Mortars
- 3X Mortar Sections
- ATGM Platoon
- 4X ATGM Detachments (1Xin Mountain Infantry Regiments)
- 1X ATGM launcher and missiles (5km? range)
- 1X ATGM launcher and missiles (2.5km range)
- 4X ATGM Detachments (1Xin Mountain Infantry Regiments)
- Signals Platoon
- Radio Section
- Line Section
- Pioneer Platoon
- 2X Assault Section
- Pioneer Section
- Company HQ
- 4X Rifle Coy
- Company HQ
- O.C. (Officer Commanding)[Major]
- Second in Command[Captain]
- ?
- 3XPlatoon
- Platoon HQ
- Platoon leader[Subedar/ Lt.]
- 3XSection
- Assault Group
- Section leader [Naik]
- 5X Riflemen
- LMG Group
- Section second in command [Lance Naik]
- 2X LMG gunner
- RCL operator
- Assault Group
- Platoon HQ
- Company HQ
- HQ Company (Coy)
Questions that remain:-
- Question marks in above list.
- Composition of HQ at each level.
- Who commands the Platoon in Rifle Companies? A Subedar or a Lt.?
- Who has the UAV, BFSR? Battalion Intel section?
- Where are AGL, MBGL and 51 mm mortar? Platoon HQ of rifle companies?
- Where are snipers posted?
- Number and make of vehicles available with Transport Platoon?
- Where is the Ghatak platoon?
- Will line sections of Signals platoon be retained after Software Defined Radios are introduced into service?
- Job of Assault Pioneer Section to breach obstacles and lay mines?
Last edited:



