"Cold" launch of a CZ 11 rocket carrying 6 satellites. Interesting capability military wise:
http://www.eastpendulum.com/6-satellites-chinois-et-canadien-mis-en-orbite-par-le-lanceur-cz-11
6 Chinese and Canadian satellites put into orbit by CZ-11 launcher
The Jiuquan Space Center (JSLC) yesterday completed its 100th civilian launch, allowing the new Chinese CZ-11 launcher from the Long March family to put into orbit six satellites, including one Canadian.
The takeoff, carried out from a Tractor-Erector-Launcher car on a simplified shooting step, took place this Friday 19 January at 12:12 Beijing time. This is the third flight of CZ-11, which has made a flawless run so far since its maiden flight in September 2015.
Among the six passengers of this fourth Chinese space launch in 2018 are two video satellites 07 and 08 of the
Jilin-1commercial observation constellation , two CubeSat 6U from the Tianyi Private Institute known as
XJNA (
Xiao Jiang New Area ) and QTT-1, as well as a
Huai'an ZHOU En Lai CubeSat 2U designed by Nanjing University of Science and Technology and
middle school students from Jiangsu Province, and Kepler Communication's CubeSat 3U Canadian
KIPP .
The third flight of the CZ-11 launcher
Developed by CASC Group's Chinese Casting Technology Academy (CALT), the CZ-11 is the only solid propellant rocket in the Long March launchers family. It is a four-stage launcher, all running on solid propellant, which measures 20.8 meters long, 2 meters in diameter and weighs about 58 tons with a take-off thrust of 120
The program, which is part of the new generation Chinese launchers, started development in 2012 and achieved its inaugural flight on September 25, 2015 by placing 4 satellites in SSO orbit.
Like its main competitors , CASIC's
Kuaizhou rockets , CASC's CZ-11 has been designed to provide a means of rapid access to space and address the small satellite segment of the domestic and international market, with a capacity of 400 kg in a 700-kilometer SSO orbit. The preparation of CZ-11 before its launches is particularly short - in 24 hours the rocket could be ready and in flight according to its designers.
But this very short period of preparation remains theoretical for the moment and has not yet had the opportunity to demonstrate it. For this launch, for example, the two main satellites Jilin-1-07 and -08 left their factory on January 1st and the integration was completed on the 13th, for a launch on the 19th. So we see a much shorter duration compared to a conventional launcher liquid propellant, but it is still far from the account of 24 hours announced.
Unlike most civilian rockets that launch from a firing point, the CZ-11 takes off from a TEL (Tractor-Erector-Launcher) as a ballistic missile. It is perhaps for this reason that the photos of his first two launches in 2015 and 2016 are unveiled only recently, on the occasion of this third flight.

The CZ-11 Y3 launcher

The integration of satellites to the launcher

The CZ-11 is ejected outside its launch tube by a gas generator

According to
a statement issued by the CASC group , the CALT Institute has made several improvements to the launcher to increase its carrying capacity by around 20%.
One of them consists of a completely revisited cap made of carbon-carbon composite, with a new coating laid by automated machines that can significantly reduce its thickness.
A new satellite separation support has also been developed at the request of customers, with one exception, the Canadian KIPP satellite, which has used its own separation system provided by the Dutch company SLS.
The Chinese authorities have issued two messages to aircrew (NOTAM) to report a fallout area of the launcher debris. It is located about 320 km from the firing point and could correspond to the drop zone for the first floor or the headdress.
A0223 / 18
Q) ZLHW / QRTCA / IV / BO / W / 000/999 / 3809N09931E034
A) ZLHW B) 1801190407 C) 1801190425
E) A TEMPORARY RESTRICTED AREA ESTABLISHED BOUNDED BY:
N373645E0994253-N374351E0990304-N384153E0991924-N383442E0995943
BACK TO START. VERTICAL LIMITS: GND-UNL
F) GND G) UNL
A0240 / 18
Q) ZLHW / QARLC / IV / NBO / E /
000/999 / A) ZLHW B) 1801190402 C) 1801190427
E) THE FLOW SEGMENTS OF ATS RTE CLSD:
1. W191: MULRU - RUSAT.
2. B215: NOGEX - OMGUP.

NOTAMs for the 3rd flight of CZ-11 (Image: East Pendulum)
It should be noted that the CZ-11 launcher did not fly by relying on an umbilical tower as for the other classic Long March rockets, because of its concept called "rapid reaction" originally from the middle military and its particular mode of preparation.
For this purpose, the JSLC Space Center constructed two new, very simplified firing points, located respectively 4.3 and 6 km from the main launch site, each with concrete ground and lightning arresters. One for the CASC CZ-11 and the other for the Kuaizhou CASIC launchers.
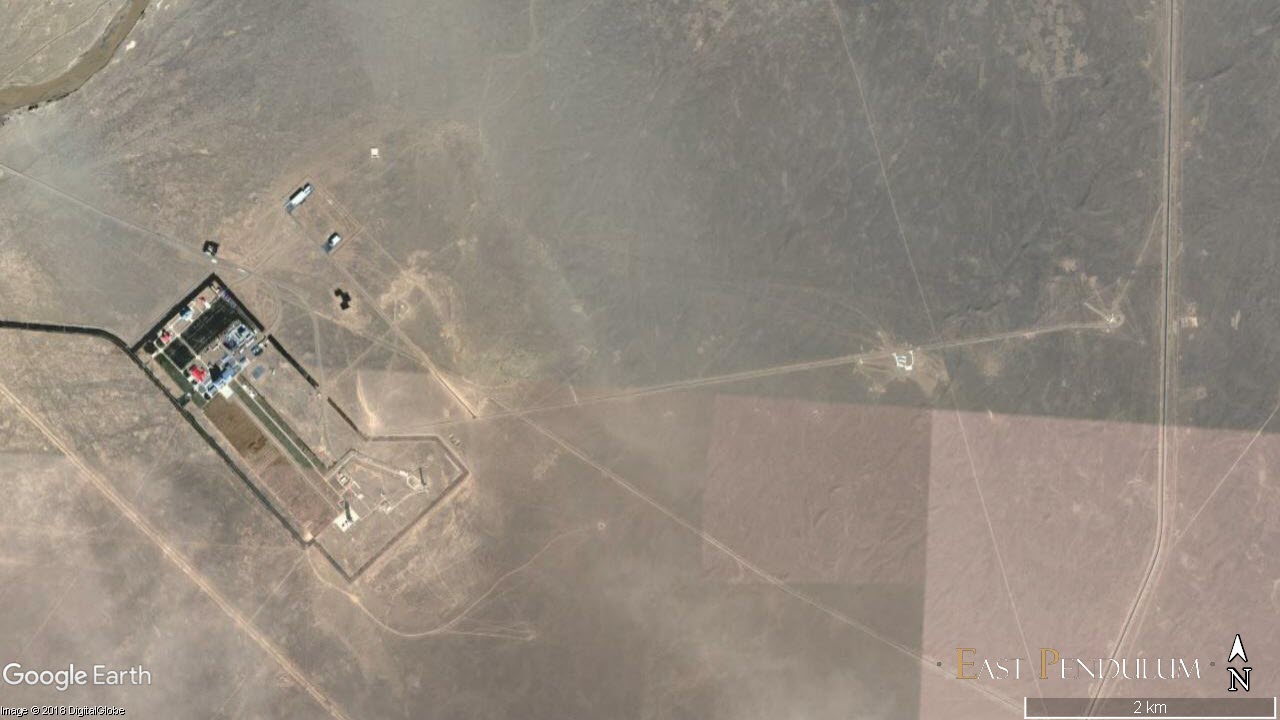

The site of Jiuquan Space Center and the two firing steps by extension
Jilin-1 video satellites and the four CubeSats
The main passengers of this CZ-11 flight are the two satellites Jilin-1-07 and Jilin-1-08, both of which are part of the Jilin-1 commercial ground-based observation constellation, which will be networked with the 8 first satellites put into orbit between 2015 and 2017.
Jilin-1-07 is also called "Deqing 1", Deqing being a destrict of Zhejiang Province, while Jilin-1-08 also has another name called "Silviculture 2". The two optical observation satellites weigh 416 kg together and they have cameras with a maximum resolution of 0.92 meters with a swath of 19 km.
Their theoretical life is more than 3 years according to the manufacturer Chang Guang Satellite Technology.

The Jilin-1-07 satellite (Deqing 1)
After these two satellites as main payloads come four nano-satellites, including two CubeSats 6U, a 3U and a 2U.
The two 6U XJNA and QTT-1 satellites are all designed by the Tianyi Institute (天 仪 研究院), a private satellite manufacturer in China, which weighs in at 8kg each. XJNA, also called
Xiaoxiang-2 , ships the instruments for 4 different experiments -
- Optical fiber remote sensing, developed by Beijing Information Science & Technology University
- Software radio trials in space, co-developed with a subsidiary of the CALT Institute
- The amateur radio tests, conducted by Hunan Radio Association which brings together a group of radio amateurs
- Optical image stabilization tests, co-developed with Xi'an Jiaotong University
The QTT-1, meanwhile, was commissioned by the company Quan Tu Tong (全 图 通 位置 网络 限 有限公司), specializing in geolocation services based on the Chinese navigation system Beidou. The experimental nano-satellite includes an integrated navigation system, a small commercial camera, an AIS transponder for ships and a radio test bench for amateurs. Quan Tu Tong plans to offer its satellite "self-service" so that users can exploit it to other types of tests in orbit.
Note that the Tianyi Institute had signed a launch contract with the CALT Institute for 30 of its satellites, XJNA and QTT-1 are therefore parties.
The fifth passenger of the CZ-11 flight is still a Chinese nano-satellite named after former Chinese premier ZHOU En Lai and his birthplace Huai'an. Designed by Nanjing University of Science and Technology, with the participation of college and high school students from Jiangsu Province, the CubeSat 2U weighing 2.4 kg will be used to conduct space experiments for young people, and especially test a desorbitalization device.
This is a "sail" made of double-sided aluminized polyimide film, which measures approximately 1.2 m² and weighs 300 g. When folded it is only Ø 70 mm × 60 mm.
The sixth and final passenger comes from a Canadian startup, Kepler Communications, which wants to commercialize inter-satellite communication services and a network of connected objects (IoT) in the maritime, agricultural and transportation sectors. The satellite is team including a software radio.
For the time being NORAD has listed 10 objects in orbit, the satellites should have been placed in an orbit of 611 km x 627 km x 86.69 °.
2018-008A
1 43155U 18008A 18020.21592346 -.00000065 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9999
2 43155 97.5385 97.1182 0016649 294.4594 85.3923 15.10300244 154
2018-008B
1 43156U 18008B 18020.16323142 -.00000064 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9999
2 43156 97.5467 97.0633 0013187 292.6507 158.8889 15.09742579 149
2018-008C
1 43157U 18008C 18020.16323850 -.00000064 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9996
2 43157 97.5469 97.0638 0014217 283.6051 167.0643 15.09476038 140
2018-008D
1 43158U 18008D 18020.16386288 -.00000064 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9991
2 43158 97.5447 97.0564 0012715 296.3020 157.7086 15.09471992 122
2018-008E
1 43159U 18008E 18020.29367387 -.00000064 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9995
2 43159 97.5400 97.1922 0013256 281.8266 156.6536 15.09340953 156
2018-008F
1 43160U 18008F 18020.16334416 -.00000064 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9990
2 43160 97.5401 97.0661 0012963 283.4685 167.2901 15.09340706 133
2018-008G
1 43161U 18008G 18020.20084029 .00008866 00000-0 16582-2 0 9990
2 43161 98.4870 97.0901 0377848 196.1307 162.7903 14.28059101 158
2018-008K
1 43164U 18008K 18019.36000805 .00000474 00000-0 10000-3 0 9995
2 43164 98.4846 96.2624 0377285 198.6156 160.0679 14.28033224 26
Historical statistics
Statistically, this launch of CZ-11 is the 4ᵉ Chinese space launch in 2018, the 3ᵉ for the CZ-11 launcher, and the 264ᵉ for the Long March launchers family.
For now, the Long March rockets of the CASC group have 253 successes and 11 failures, a success rate of 95.83%.
This is the tracking chart of all Chinese space launches since the first of 1970, including those not performed by Long March launchers, as well as the number of launches for each of the 4 Chinese space centers -

The number of launches per year for the 4 Chinese space centers (Image: East Pendulum)