WolfPack86
Senior Member
- Joined
- Oct 20, 2015
- Messages
- 10,513
- Likes
- 16,960
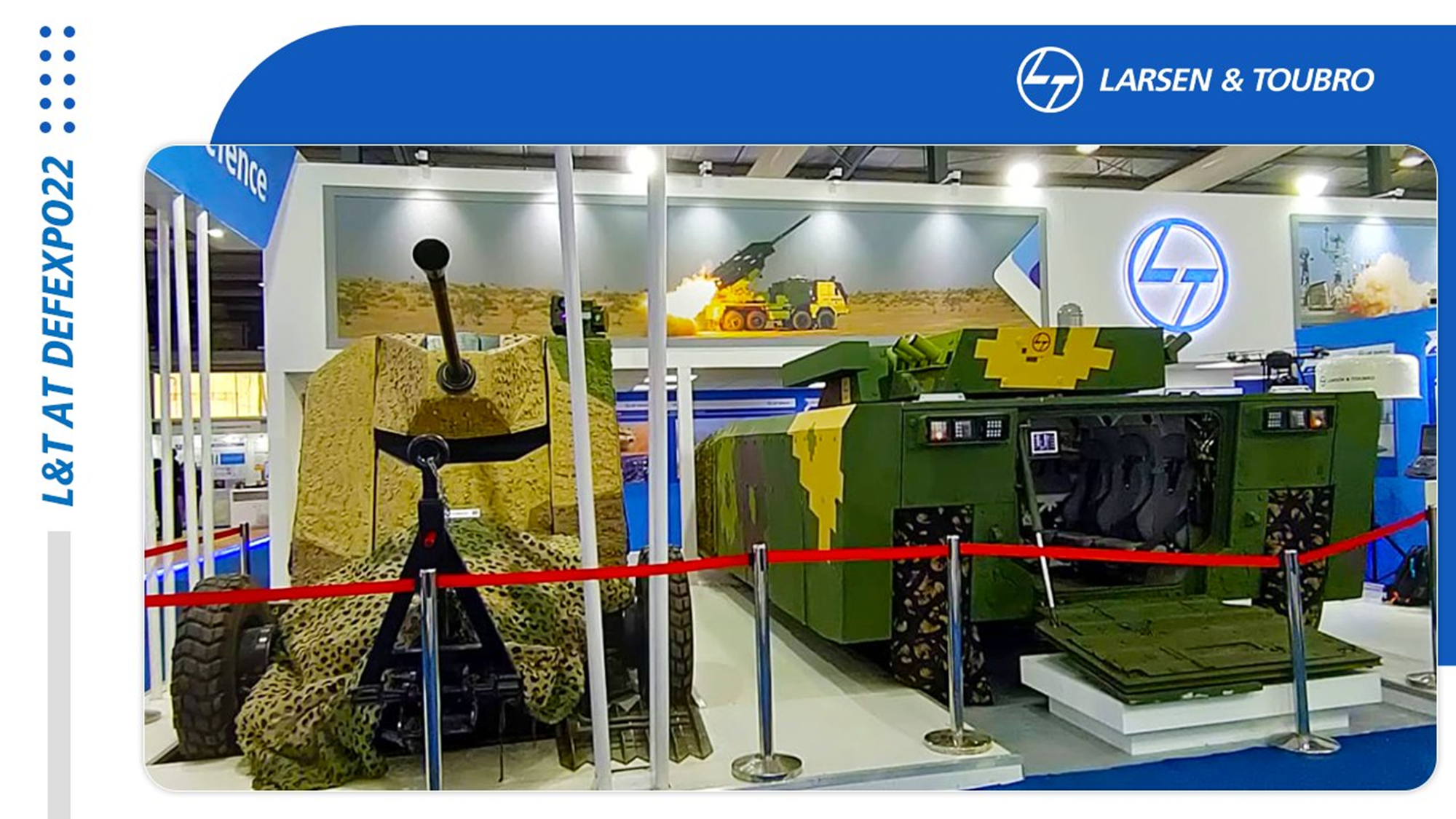
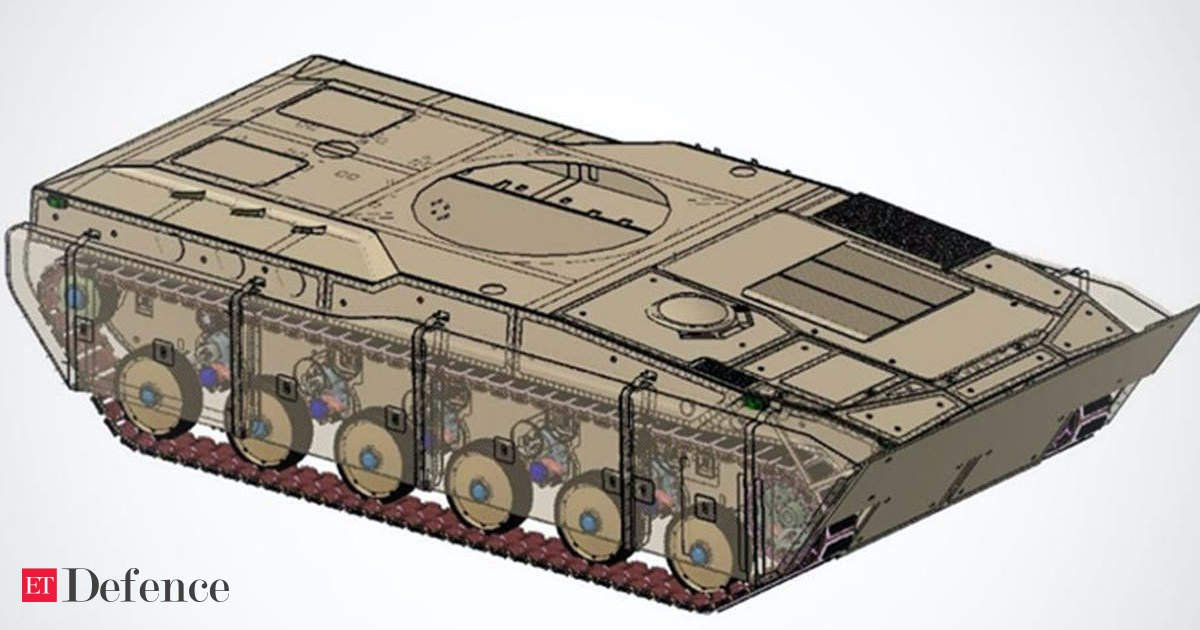
FICV developed by OFB Medak
The RFI issued by the Indian Army specifies that it intends to procure up to 1,750 FICVs in three versions.
The three versions are a 'gun version', a command version and a command and surveillance version. The
'gun version', which is primarily meant for combat operations, will constitute the bulk of the intended order
quantity (55 per cent). Command versions of infantry combat vehicles are used by battlefield commanders
to direct operations and correspond with superiors.
Broad Operational Requirements laid down in the RFI
FICV will have amphibious capability in terms of mobility
FICV will have high protection levels in the frontal arc at STANAG 5 against 25mm APDS, which can be
upgraded to STANAG 6 against 30mm APFSDS, with removable armour panels. It also lays down STANAG
4, against 14.5mm AP, on the sides & top as also STANAG 3B, 8kg mine explosive under belly.
FICV should have a power to weight ratio of 30HP/Ton
the gun version of the FICV should be capable of housing a crew of three and carrying at least eight
soldiers, the remaining two variants should have a crew of three and should carry four soldiers.
FICV should be equipped with at least a 30mm main gun and anti-tank missiles.
Command versions of the FICV should be capable of carrying drones for surveillance and also suicide
strike missions (known as 'loitering munitions').
New systems like loitering munitions and mini-UAV for targeting and battlefield awareness
The main Indian contenders are The Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), BEML, Mahindra Defence, Ashok
Leyland, Larsen and Toubro, Reliance, Bharat Forge and others. DRDO has also developed an FICV platform
called Abhay.
 anyflip.com
anyflip.com
The RFI issued by the Indian Army specifies that it intends to procure up to 1,750 FICVs in three versions.
The three versions are a 'gun version', a command version and a command and surveillance version. The
'gun version', which is primarily meant for combat operations, will constitute the bulk of the intended order
quantity (55 per cent). Command versions of infantry combat vehicles are used by battlefield commanders
to direct operations and correspond with superiors.
Broad Operational Requirements laid down in the RFI
FICV will have amphibious capability in terms of mobility
FICV will have high protection levels in the frontal arc at STANAG 5 against 25mm APDS, which can be
upgraded to STANAG 6 against 30mm APFSDS, with removable armour panels. It also lays down STANAG
4, against 14.5mm AP, on the sides & top as also STANAG 3B, 8kg mine explosive under belly.
FICV should have a power to weight ratio of 30HP/Ton
the gun version of the FICV should be capable of housing a crew of three and carrying at least eight
soldiers, the remaining two variants should have a crew of three and should carry four soldiers.
FICV should be equipped with at least a 30mm main gun and anti-tank missiles.
Command versions of the FICV should be capable of carrying drones for surveillance and also suicide
strike missions (known as 'loitering munitions').
New systems like loitering munitions and mini-UAV for targeting and battlefield awareness
The main Indian contenders are The Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), BEML, Mahindra Defence, Ashok
Leyland, Larsen and Toubro, Reliance, Bharat Forge and others. DRDO has also developed an FICV platform
called Abhay.
DefINsights - Sugosha Media Jul 2021 - Flip eBook Pages 1-24 | AnyFlip
View flipping ebook version of DefINsights - Sugosha Media Jul 2021 published by sohilpat on 2022-01-09. Interested in flipbooks about DefINsights - Sugosha Media Jul 2021? Check more flip ebooks related to DefINsights - Sugosha Media Jul 2021 of sohilpat. Share DefINsights - Sugosha Media Jul...