India's Space based Telescopes and Astronomical spacecraft
- Thread starter Indx TechStyle
- Start date
More options
Who Replied?Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChastE)
The objective of the instrument is to carry out in-situ measurements of temperature profile on the lunar surface to derive the vertical temperature gradient up to a depth of 100 mm near the polar region. This is carried out by means of inserting a probe with thermal sensors into the lunar regolith using a motor based mechanism.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
NIUSAT in Clean Room.
The cleanroom, filters out unwanted particles by feeding in HEPA-filtered air in through air vents and drawing away dirty air through floor-level vents. The cleanrooms are also kept at a positive pressure with air locks that prevent the ingress of outside air.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
Calibration and Space Qualification for Polix.
Vibration tests on the detector at ISRO qualification levels is planned and a jig for holding the detector on the vibration table has been fabricated. In order measure the actual collimator response, a collimator calibration jig has been fabricated, which can scan the collimator in front of a X-ray source at different angles.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) based Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity Studies.
The payload is a part of Lander of Chandrayaan 2 mission and is termed as Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity Studies (ILSA). The instrument has indigenously developed silicon micromachined Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) based sensing elements.
The ILSA instrument is a single package containing seismometers with output from three axes. The sensing elements are high sensitivity capacitive accelerometers. Each axis will have two sensor chips, one chip meant for measurement in fine range and the other meant for coarse range. The sensors have different mechanical sensitivities. This is the practical approach adopted to achieve the very wide dynamic range of operations for the seismometers required. Preprocessing electronics with MEMS sensors is packaged in a Hybrid Micro Circuit (HMC) package. Three HMC’s
are mounted in orthogonal direction such that the sensor sensitive axes are along X, Y and Z directions. The processing circuits, power regulators and clock generating circuits are implemented in PCBs. All are integrated and housed in a mechanical package forming the instrument. ILSA can resolve upto 100 nano-g Hz-½ and has a dynamic range of ±0.5 g, where g is 9.8 ms-2. It has a bandwidth of 40 Hz. It weighs 1.5 Kg, consumes <4 W power and has dimensions 170 x 170 x 72 mm and provides digital output.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
GSAT-17 Undergoing Vibration Test
Rocket boosters and spacecraft are subject to intense acoustic environments during launch, which induce high levels of vibration in structural elements and equipment. In addition, elastic structural interactions with propulsion systems and flight control systems can produce low-frequency,
high-deflection flight instabilities.
Ground testing to simulate launch-induced vibration or to investigate structural dynamic characteristics has proven to be vital in developing successful spacecraft programs.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
Keplerian disk with a CENBOL surface at the inner edge being viewed in X-rays at 36deg, 50deg and 80deg respectively. At the bottom-left, one can see the Keplerian component through CENBOL
ICSP workers are contributing to the detection of black hole horizon by computing expected images of invisible black holes surrounded by accretion disks. They have successfully computed images of two component advective flows (TCAF). This gives the most accurate description of black hole accretion process to date. Images of disks along with jets were obtained. Results indicate that disks in soft states when viewed at low inclination angle may allow one to resolve the horizon if the beam width is small enough.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
GISAT-1 is the first of two earth observation satellites of India (launch postponed), it can also provide ballistic missile early-warning. GISAT-1 will carry a high-resolution camera. The imaging payload consists of multi-spectral (visible, near infra-red and thermal), multi-resolution from 40 metres to 1.5km. This means that GISAT-1 will be able to send a selected sector-wise image every 5 minutes and an image of the entire Indian landmass every 30 minutes at 50-metre spatial resolution.
The geo imaging satellite will help keep a check on natural hazards and disasters, keep a constant watch on the border areas, and monitor any geographical changes. It will be able to carry out rapid surveillance. It will rotate the earth and return the same spot every two hours and when needed, it can spend a longer time on certain areas.
The GISAT-1 has a lifespan of 7 years, weighs 2,275kg, and the main equipment it is carrying is the multi- and hyper-spectral imager along with the 700mm Ritchey-Chretien telescope to carry out its function of earth observation and data collection. The GISAT-1’s mission payload comprises:
700mm Ritchey-Chretien telescope based on the design of Cartosat 2.
Array detectors in VNIR, SWIR and LWIR bands.
High-resolution multi-spectral VNIR (HRMX-VNIR): 50-metre resolution.
High-resolution multi-spectral (HRMX-LWIR): 1.5km resolution.
Hyper-spectral VNIR: 320-metre and 192-metre resolution.
Hyper-spectral SWIR: 320-metre and 192-metre resolution.
Data handling system and camera electronics.
Transmit antenna system which is electronically steerable.
High agility platform to enable large payload steering requirements.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
FADS for RLV.
Flush air data sensing system (FADS) forms a mission-critical subsystem in re-entry vehicles. It makes use of surface pressure measurements from the nose cap of the vehicle for deriving air data parameters such as angle of attack, angle of sideslip, Mach number, etc. of the vehicle. These parameters are used by the flight control and guidance systems, and also assist in the overall mission management.
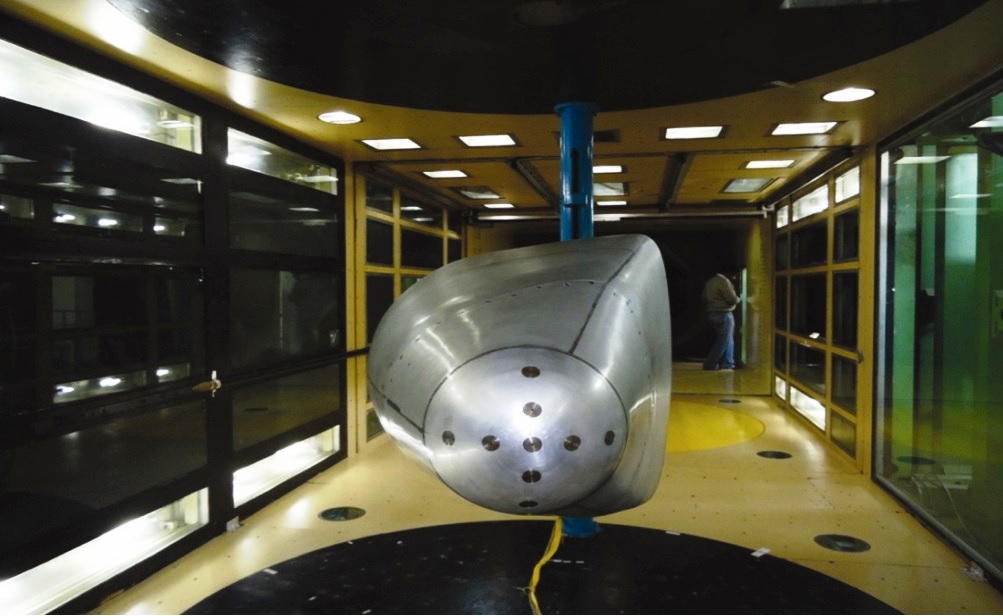
End-to-end system of FADS housed inside the nose cone.
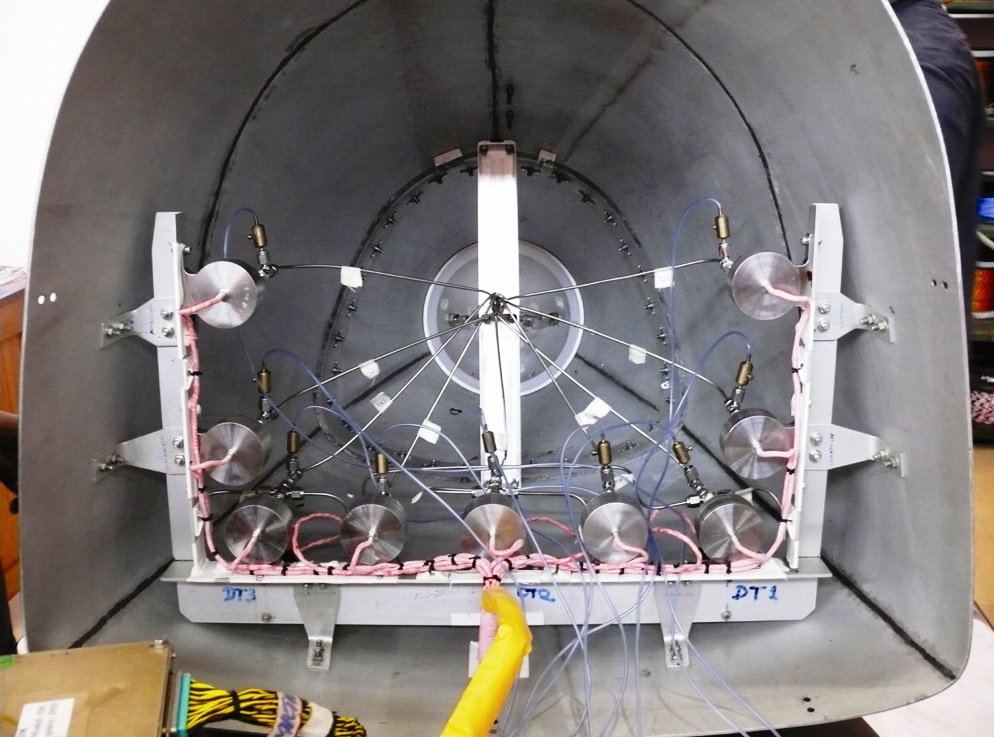
Flush air data sensing system tubing and pressure sensor.
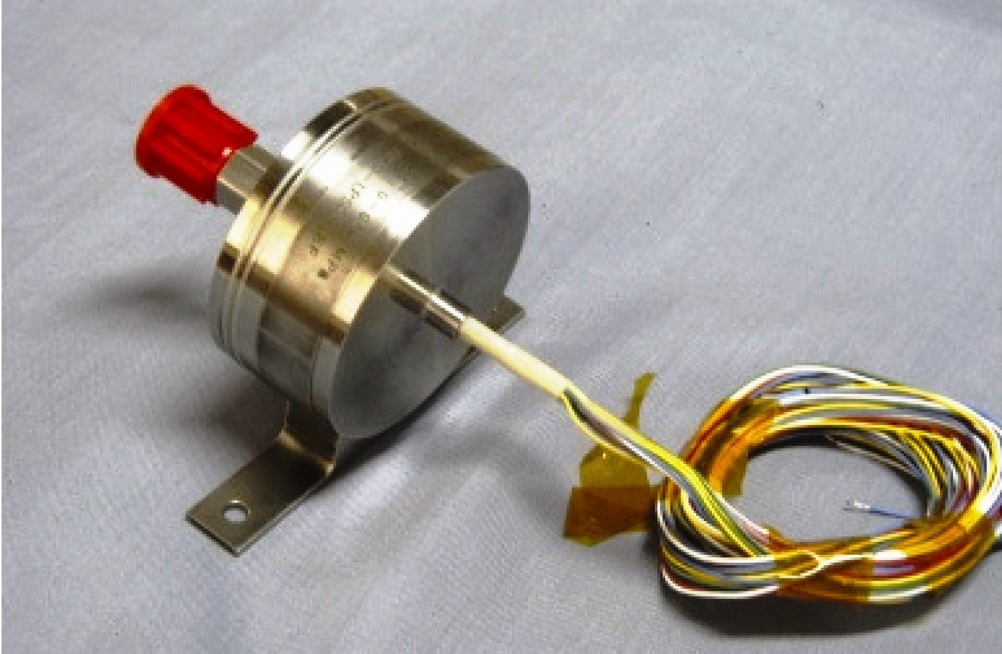
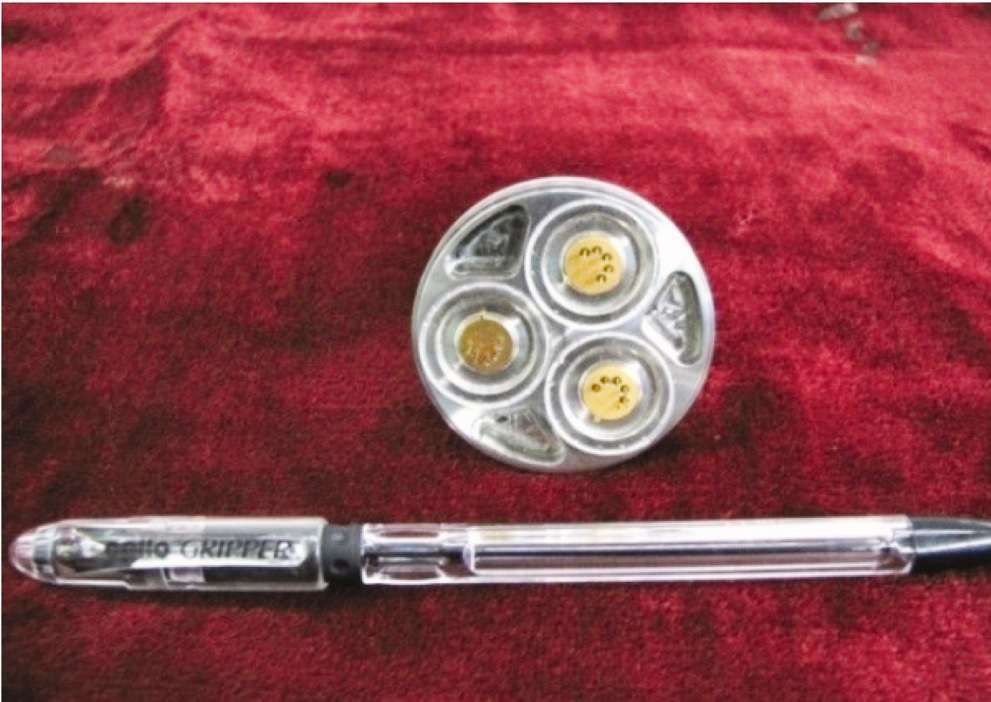


Absolute pressure transducer used in the system.
Flush air data sensing system (FADS) forms a mission-critical subsystem in re-entry vehicles. It makes use of surface pressure measurements from the nose cap of the vehicle for deriving air data parameters such as angle of attack, angle of sideslip, Mach number, etc. of the vehicle. These parameters are used by the flight control and guidance systems, and also assist in the overall mission management.
End-to-end system of FADS housed inside the nose cone.
Flush air data sensing system tubing and pressure sensor.
Absolute pressure transducer used in the system.
- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,286
- Likes
- 56,234
The thread is about Indian space telescopes though. Not RLV or Human spaceflight.
Karthi
Senior Member
- Joined
- Jul 15, 2018
- Messages
- 2,214
- Likes
- 17,753
3.6m Optical Telescope at Devasthal, Nainital.
some of the science drivers of DOT are
- Studying magnetic field structure of stars
- Studying chemical evolution of Milky -Way via stellar ISM abundance
- The search for extra solar planets
- Kinematics of stars in the outer region and the halo of the Milky-Way
- Polarization properties of BL-Lac and other galactic nuclei
- NIR spectroscopy and narrow band imaging of the galactic HII regions and star clusters to understand the formation of stars and their evolution in different environment
- Optical spectroscopy and deep time resolved imaging of galactic X-Ray binaries to understand the kinematics of accretion disk
- NIR spectroscopy of debris around stars to understand planet formation
Latest Replies
-
CNSA news, Updates and Discussions
- smooth manifold
-
China Economy: News & Discussion
- Cheepek
-
Idiotic Musings From Firangistan
- Blademaster
-
DRDO, PSU and Private Defence Sector News
- Truthsoldier
-
Indian Special Forces
- rkhanna
-
Jokes Thread
- The Juggernaut
-
North East Security Watch
- tomthounaojam
-
China Space Station-Tiangong
- smooth manifold
-
Indian Economy: News and Discussion
- sameer3694
Global Defence
-
Small arms and Light Weapons
- Zoid Raptor
-
Aircraft Crash Notification
- NutCracker
-
Drone swarms -India
- LETHALFORCE
-
Turkish defense industry news updates
- tfxkaanf23
-
F-35 Joint Strike Fighter
- blackjack
-
World Military/Paramilitary/Special Forces
- airborneCommando
-
New Naval Technology
- Blademaster
-
F-16 Viper
- MiG-29SMT
New threads
-
World Chess Championship 2024
- SwordOfDarkness
- Replies: 4
-
Chinese Lunar Exploration Program
- skywatcher
- Replies: 0
-
Boston Dynamics showed flexible new robot Atlas
- Soldier355
- Replies: 1
Articles
-
India Strikes Back: Operation Snow Leopard - Part 1
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 9
-
Aftermath Galwan : Who holds the fort ?
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 33
-
The Terrible Cost of Presidential Racism(Nixon & Kissinger towards India).
- ezsasa
- Replies: 40
-
Modern BVR Air Combat - Part 2
- mist_consecutive
- Replies: 22
-
Civil & Military Bureaucracy and related discussions
- daya
- Replies: 32
