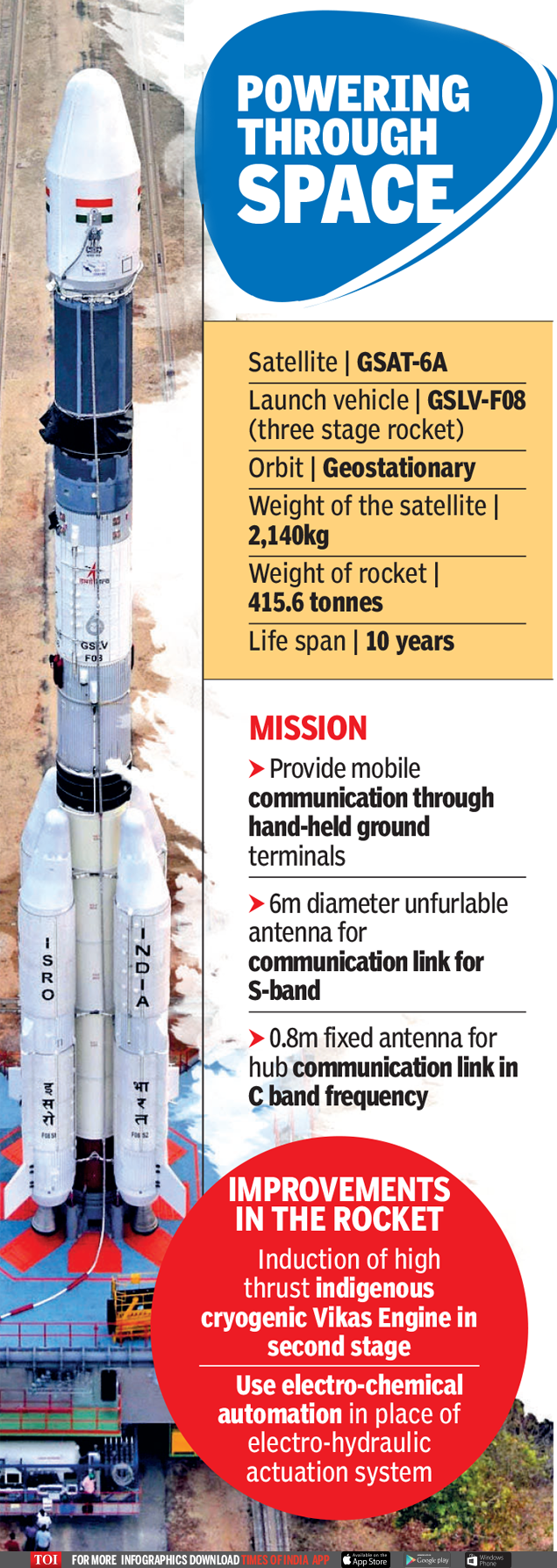
Isro set to place GSAT-6A in orbit today, crucial step for armed forces and moon mission
CHENNAI: When GSLV Mk-II successfully places communication
satellite GSAT-6A in to orbit on Thursday, it will give Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) and the Indian Armed Forces a shot in the arm.
Isro will be testing certain critical systems that may eventually go into the country’s second lunar mission, and the satellite will enhance communication services for the Indian military.
Isro sources said they will be validating systems including high thrust Vikas engine, which may eventually be used during the launch of Chandrayaan-2. The improved engine, which powers the second stage of the launch vehicle, will be able to carry more weight adding another 70kg to its payload capability, said officials. “Any improvement in the vehicle will be usually incorporated in the subsequent launches,” said an Isro official. “As of now, Chandrayaan-2 is planned for October this year.”
GSLV Mk-II (GSLV-F08), carrying communication satellite GSAT-6A weighing 2,140kg, is expected to take off from the second launch pad in Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, at 4.56pm. It will be GSLV’s 12th flight and sixth with an indigenous cryogenic engine.
Scientists will also be testing electro-mechanical actuation system in the place of a electro-hydraulic actuation in an effort to enhance the reliability of the launch vehicle. An actuator is a component that controls the vehicle in every stage.
GSAT-6A, which the rocket will carry, will be different from the usual communication satellites. While it will complement its predecessor GSAT-6, Isro sources said, “The satellite will provide services for
defence purposes and will not add any transponder capacity for general uses.” GSAT-6 has been in orbit providing communication services since its launch on August 27, 2015
The satellite will be have a 6m wide unfurlable antenna, thrice the size of the antenna generally used by Isro satellites, which will enable mobile communication from anywhere through hand-held ground terminals.
During the launch mission, the three-stage GSLV will eject the satellite into a geostationary transfer orbit at an altitude of about 35,975km from earth at about 17 minutes after liftoff. Post the launch, Isro scientists will conduct three orbital raising manoeuvres by firing the thrusters onboard the satellite from the ground station in the subsequent days to place it in its final orbital slot at an altitude of about 36,000km.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com...com&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=TOIDesktop